Application of Ultrasound Localization Microscopy in Evaluating the Type 2 Diabetes Progression
- PMID: 40066372
- PMCID: PMC11893074
- DOI: 10.34133/cbsystems.0117
Application of Ultrasound Localization Microscopy in Evaluating the Type 2 Diabetes Progression
Abstract
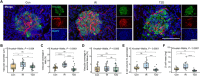
Type 2 diabetes is considered as a chronic inflammatory disease in which the dense microvasculature reorganizes with disease progression and is highly correlated with β cell mass and islet function. In this study, we constructed rat models of type 2 diabetes and used ultrasound localization microscopy (ULM) imaging to noninvasively map the pancreatic microvasculature at microscopy resolution in vivo to reflect β cell loss and islet function deterioration, and evaluate the efficacy after anti-cytokine immunotherapy. It was unveiled that ULM morphological and hemodynamic parameters have a strong link with β cell loss and deterioration of pancreatic islet function. This correlation aligns with the observed pathological alterations in the microvessels of islet and demonstrated that ULM can effectively mirror the functionality of β cells during rapid fluctuations in blood glucose levels by observing changes in mean velocity. Furthermore, it was revealed that treatment with anti-cytokine immunotherapy enhances the function and health of β cells by restoring the microvascular environment. Remarkable improvements in vessel morphology (measured by fractal dimension) and hemodynamics (indicated by mean velocity and vessel density) were noted following the anti-cytokine immunotherapy, signifying a significant enhancement at the treatment's conclusion (P < 0.05). These observations suggested that ULM technology holds promise as a visible and efficient tool for monitoring the effectiveness of anti-cytokine immunotherapy in managing type 2 diabetes. Pancreatic microvessel-based ULM may serve as a novel noninvasive method to assess β cells, providing a valuable clinical tool for tracking the progression of type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2025 Tao Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Donath MY, Shoelson SE. Type 2 diabetes as an inflammatory disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011;11(2):98–107. - PubMed
-
- Yang J, Zhang LJ, Wang F, Hong T, Liu Z. Molecular imaging of diabetes and diabetic complications: Beyond pancreatic beta-cell targeting. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019;139:32–50. - PubMed
-
- Siehler J, Blochinger AK, Meier M, Lickert H. Engineering islets from stem cells for advanced therapies of diabetes. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021;20(12):920–940. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

