Amyloid-like DNA bridging: a new mode of DNA shaping
- PMID: 40066879
- PMCID: PMC12257945
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaf169
Amyloid-like DNA bridging: a new mode of DNA shaping
Abstract
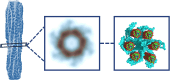
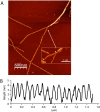
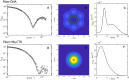
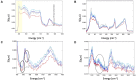
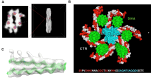
All organisms depend on specific proteins to compact and organize their genomes. In eukaryotes, histones fulfil this role, while bacterial chromosomes are shaped by nucleoid-associated proteins (NAPs). Among its pleiotropic functions, the NAP Hfq plays a pivotal role in bacterial genome organization. In this study, we characterized the structure of the C-terminal extension of Hfq, which mediates chromosomal compaction, in its DNA-bound state. Using an integrative approach that combined transmission electron microscopy, neutron scattering, site-directed mutagenesis, and molecular modeling, we identified an amyloid module formed by the C-terminal region of Hfq. This module uniquely bridges and compacts six DNA molecules, marking the first documented instance of an amyloid structure with DNA-bridging properties. Our findings redefine the functional landscape of amyloids, linking them to genome architecture and gene regulation. This result suggests that amyloid-DNA interactions may represent a conserved mechanism across biological systems, with profound implications for understanding genome organization and the regulation of gene expression in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Dorman CJ Function of nucleoid-associated proteins in chromosome structuring and transcriptional regulation. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014; 24:316–31. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

