Biaryl Phosphates and Phosphonates as Selective Inhibitors of the Transcription Factor STAT4
- PMID: 40067743
- PMCID: PMC12087874
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202504420
Biaryl Phosphates and Phosphonates as Selective Inhibitors of the Transcription Factor STAT4
Abstract
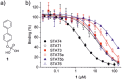
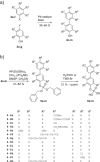
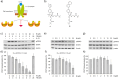
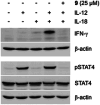
The transcription factor STAT4 has been implicated in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases, including inflammatory bowel disease, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and diabetes mellitus. Here, we report p-biaryl phosphates and phosphonates as the first small-molecule inhibitors of STAT4. The most potent p-biaryl phosphate inhibited the protein-protein interaction domain of STAT4, the SH2 domain, with submicromolar potency (Ki = 0.35 µM) and 14-fold selectivity over the closely related family member STAT3, which has the same core peptide binding motif as STAT4. Further development resulted in the phosphatase-stable inhibitor Stafori-1, which protected STAT4 but not STAT3, against thermal denaturation in cell lysates. Its cell-permeable prodrug Pomstafori-1 selectively inhibited STAT4 phosphorylation in cultured human cells at low micromolar concentrations. Our data open up the possibility of exploring STAT4 as a target protein for small molecules in the treatment of unmet medical needs.
Keywords: Biological activity; Inhibitors; Protein–protein interactions; SH2 domains; Transcription factors.
© 2025 The Author(s). Angewandte Chemie International Edition published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Levy D. E., J. E. Darnell, Jr. , Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 651–662. - PubMed
-
- Visconti R., Gadina M., Chiariello M., Chen E. H., Stancato L. F., Gutkind J. S., O'Shea J. J., Blood 2000, 96, 1844–1852. - PubMed
-
- Szabo S. J., Sullivan B. M., Peng S. L., Glimcher L. H., Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 21, 713–758. - PubMed
-
- Liang Y., Pan H. F., Ye D. Q., Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2014, 18, 945–960. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

