Nutritional therapy in palliative care units: A bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 40068025
- PMCID: PMC11902936
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041772
Nutritional therapy in palliative care units: A bibliometric analysis
Abstract
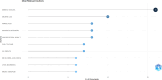
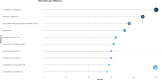
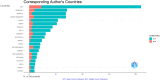
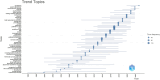
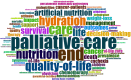
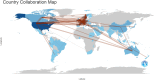
This bibliometric review aimed to provide a general picture and systematic mapping of research trends in palliative care (PC) and nutrition internationally. The Web of Science (WoS) database was searched on May 7, 2024, for original articles focusing on PC and nutrition between 1970 and 2023. Relevant publications were searched using the Thompson Reuters Science Citation Index (SCI) search engine with the keywords "palliative care," "palliative care unit," "nutrition," and "palliative care and nutrition." A total of 918 articles were found in 391 sources with the participation of 4772 authors. An average of 18.32 citations per article was identified. When analyzed by country, the United States of America (USA) had the highest number of publications (n = 210), followed by Germany (n = 71) and France (n = 69). In the list of the most frequently repeated keywords in the field of PC and nutrition, the most commonly used words were "palliative care" and "end." Other common terms included "nutrition," "quality of life," and "hydration." Additional frequently used words were "cancer," "symptoms," and "management.." This study is the first step toward analyzing and mapping research related to PC and nutrition. It shows that the number of publications related to PC and nutrition has steadily increased between 1991 and 2023. United State of America and European countries are the top publishers and receive the most citations. Hot topics in the field include "end," "nutrition," "quality of life," "hydration," "cancer," "symptoms," and "management," highlighting the complexity of the subject.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- WHO. https://www.who.int/europe/news-room/fact-sheets/item/palliative-care. Accessed March 4, 2025.
-
- Hsieh MH, Lin WC, Yeh TC, Liu CJ, Chen M, Liu CK. Bibliometric and visualized analysis of good death research from 2001-2021. Omega (Westport). 2023:302228231184301. - PubMed
-
- Shreves A, Marcolini E. End of life/palliative care/ethics. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2014;32:955–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

