mRNA lipid nanoparticle formulation, characterization and evaluation
- PMID: 40069324
- PMCID: PMC12312782
- DOI: 10.1038/s41596-024-01134-4
mRNA lipid nanoparticle formulation, characterization and evaluation
Abstract
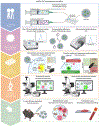
mRNA-based therapies have emerged as a cutting-edge approach for diverse therapeutic applications. However, substantial barriers exist that hinder scientists from entering this research field, including the technical complexity and multiple potential workflows available for formulating and evaluating mRNA lipid nanoparticles (LNPs). Here we present an easy-to-follow and step-by-step guide for mRNA LNP formulation, characterization and in vitro and in vivo evaluation that could lower these barriers, facilitating entry for scientists in academia, industry and clinical settings into this research space. In this protocol, we detail steps for formulating representative mRNA LNPs (0.5 d) and characterizing key parameters (1-6 d) such as size, polydispersity index, zeta potential, mRNA concentration, mRNA encapsulation efficiency and stability. Then, we describe in vitro evaluations (3-6 d), such as protein expression, cell uptake and mechanism investigations (3-5 d), including endosomal escape, as well as in vivo delivery evaluation (2-3 d) encompassing intracellular and secreted protein expression levels, biodistribution and additional tolerability studies (1-2 weeks). Unlike some alternative protocols that may focus on discrete aspects of the workflow-such as formulation, characterization or evaluation-our protocol instead aims to integrate each of these aspects into a simplified, singular workflow applicable across multiple types of mRNA LNP formulations. In describing these procedures, we wish to disseminate one potential workflow for mRNA LNP production and evaluation, with the ultimate goal of furthering innovation, collaboration and the translational advancement of mRNA LNPs.
© 2025. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill has filed some patents on data related to this work, with the authors named as inventors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Nucleic Acid Nanocapsules as a New Platform to Deliver Therapeutic Nucleic Acids for Gene Regulation.Acc Chem Res. 2025 Jul 1;58(13):1951-1962. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.5c00126. Epub 2025 Jun 9. Acc Chem Res. 2025. PMID: 40491030
-
Influence of ionisable lipid and sterol variations on lipid nanoparticle properties and performance.J Control Release. 2025 Jul 20;386:114056. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2025.114056. Online ahead of print. J Control Release. 2025. PMID: 40695375
-
Factors that influence caregivers' and adolescents' views and practices regarding human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination for adolescents: a qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Apr 15;4(4):CD013430. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013430.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40232221 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
Interventions to improve safe and effective medicines use by consumers: an overview of systematic reviews.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Apr 29;2014(4):CD007768. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007768.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24777444 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
CloneFast: A simple plasmid design and construction guide for labs venturing into synthetic biology.STAR Protoc. 2025 Aug 6;6(3):104025. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2025.104025. Online ahead of print. STAR Protoc. 2025. PMID: 40773353 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kon E, Ad-El N, Hazan-Halevy I, Stotsky-Oterin L & Peer D Targeting cancer with mRNA-lipid nanoparticles: key considerations and future prospects. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol 20, 739–754 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Jeong M, Lee Y, Park J, Jung H & Lee H Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) for in vivo RNA delivery and their breakthrough technology for future applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev 200, 114990 (2023). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- P50 HD103573/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS045892/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K12 TR004416/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 1R21EB034942-01/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB)
- R21 EB034942/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

