Exploring novel non-opioid pathways and therapeutics for pain modulation
- PMID: 40070108
- PMCID: PMC11938896
- DOI: 10.1177/17448069251327840
Exploring novel non-opioid pathways and therapeutics for pain modulation
Abstract
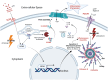
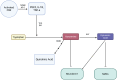
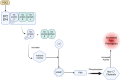
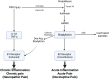
The opioid crisis has highlighted the urgent need for alternative pain management strategies. This review explores novel non-opioid targets and pathways involved in pain modulation, highlighting advancements in understanding and therapeutic potential. Pain, a multifaceted phenomenon with nociceptive, neuropathic, and inflammatory components, involves intricate molecular signaling cascades. Key pathways reviewed include voltage-gated sodium channels (Nav1.7, Nav1.8, Nav1.9), inflammasome complexes (NLRP3), the kynurenine pathway, prostaglandins, and bradykinin-mediated signaling. Emerging therapeutics such as selective Nav channel blockers, NLRP3 inhibitors, kynurenine pathway modulators, EP receptor antagonists, and bradykinin receptor antagonists offer promising alternatives to opioids. Despite challenges in clinical translation, these developments signal a paradigm shift in pain management, with precision-focused therapies poised to address unmet needs. This review emphasizes the importance of integrating molecular insights into the development of safer, more effective analgesics, setting the stage for transformative advancements in non-opioid pain relief.
Keywords: Nav; PGE2; Pain; bradykinin; inflammasome; kynurenine; non-opioid.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

