Cutaneous Hemangioma With Epithelioid Features Harboring TPM3/4::ALK Fusions : A Distinct Entity or a Molecular Variant of Epithelioid Hemangioma?
- PMID: 40070162
- PMCID: PMC12643056
- DOI: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000002380
Cutaneous Hemangioma With Epithelioid Features Harboring TPM3/4::ALK Fusions : A Distinct Entity or a Molecular Variant of Epithelioid Hemangioma?
Abstract
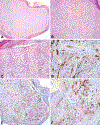
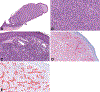
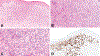
Vascular neoplasms with epithelioid cytomorphology encompass a wide spectrum of benign and malignant lesions, including epithelioid hemangioma (EH), cutaneous epithelioid angiomatous nodule (CEAN), epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (EHE), and epithelioid angiosarcoma (EAS). Recently, the first case of a cutaneous hemangioma with epithelioid features harboring a TPM3::ALK fusion was reported. Herein, we report 4 additional cases, including 1 case with an alternate TPM4::ALK fusion, and expand on the clinicopathologic and molecular genetic features of these unusual vascular lesions. Including the previously reported case, 5 tumors occurred in 4 male and 1 female patients with a median age of 14 years (range: 2 to 38 y) and involved the shoulder region (2), the lower extremity (1), trunk (1), and head and neck (1). Clinical follow-up (3 patients; 60%) showed no evidence of disease at the last follow-up (median: 5 mo; range: 1 to 16 mo). Histologically, all tumors showed highly similar morphologic features, including an epidermal collarette, well-formed vascular channels composed of epithelioid endothelial cells with intracytoplasmic vacuoles, and admixed inflammatory cells. Immunohistochemically, all tumors were positive for vascular markers such as ERG and CD31, along with strong and diffuse cytoplasmic expression of ALK. RNA sequencing revealed recurrent TPM3 exon 8 :: ALK exon 20 (4) and TPM4 exon 7 :: ALK exon 20 fusions (1). We conclude that cutaneous hemangiomas with epithelioid features harboring TPM3/4::ALK fusions show consistent morphologic, immunophenotypic, and molecular genetic features. It remains to be determined whether this neoplasm represents a distinct entity or a molecular variant of epithelioid hemangioma.
Keywords: ALK; TPM3; TPM4; cutaneous hemangioma; epithelioid hemangioma.
Copyright © 2025 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest and Source of Funding: The authors have disclosed that they have no significant relationships with, or financial interest in, any commercial companies pertaining to this article.
Figures


References
-
- Board WCoTE. Soft tissue and bone tumours. vol 5th ed. IARC Press; 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

