Co-expression of B7-H3 and LAG3 represents cytotoxicity of CD4+ T cells in humans
- PMID: 40070836
- PMCID: PMC11893609
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1560383
Co-expression of B7-H3 and LAG3 represents cytotoxicity of CD4+ T cells in humans
Abstract
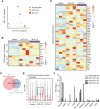
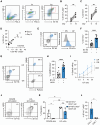
Recent studies have highlighted the potential contribution of CD4+ T cells with cytotoxic activity (CD4 CTLs) to anti-tumor immunity. However, their precise roles remain elusive, partly due to the absence of specific markers defining CD4 CTLs with target-killing potential in humans. We previously demonstrated that Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-driven immortalized B cell lines efficiently induce human CD4 CTLs with cytotoxic functions comparable to cytotoxic CD8+ T cells (CD8 CTLs). Here we show that EBV-driven CD4 CTLs exhibit prolonged proliferation and sustained cytotoxicity compared with CD8 CTLs, although their cytotoxic function markedly decreased during long-term culture. Comparative transcriptomic analysis of CD4 CTLs with varying cytotoxic activities identified B7-H3 and LAG3 as surface molecules associated with highly cytotoxic CD4 CTLs. Co-expression of B7-H3 and LAG3 correlated with CD107a expression and was observed on CD4+ T cells with enhanced cytotoxic potential in a target-dependent manner but not on CD8 CTLs. Furthermore, B7-H3+LAG3+ CD4+ T cells were induced during co-culture with bone marrow cells from pediatric patients with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL). These findings suggest that B7-H3 and LAG3 co-expression represents a characteristic feature of functional CD4 CTLs in humans, providing valuable insights into the role of CD4 CTLs in tumor immunity.
Keywords: B7-H3; CD4+ cytotoxic T cells; EB virus; LAG3; leukemia; lymphoma; tumor immunity.
Copyright © 2025 Tamura, Ohki, Nagai, Yoshizato, Nishi, Jin, Kitajima, Guo, Ichinohe, Okada, Kawano and Yasuda.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


References
-
- van Leeuwen EM, Remmerswaal EB, Vossen MT, Rowshani AT, Wertheim-van-Dillen PM, van Lier RA, et al. . Emergence of a CD4+CD28- granzyme B+, cytomegalovirus-specific T cell subset after recovery of primary cytomegalovirus infection. J Immunol. (2004) 173:1834–41. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.3.1834 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

