A mathematical model to estimate the probability of blood cultures positive for pyogenic streptococci
- PMID: 40071254
- PMCID: PMC11892445
- DOI: 10.53854/liim-3301-8
A mathematical model to estimate the probability of blood cultures positive for pyogenic streptococci
Abstract
Aims: The aim of this study was to assess the possible use of time to positivity (TTP) of blood cultures (BCs) collected at the Emergency Department (ED) to estimate the probability of pyogenic streptococci versus other Gram positive cocci in pairs and chains, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, other viridans group streptococci or enterococci.
Methods: All patients 18 years of age or older evaluated at the ED from whom BCs were collected and were positive for Gram positive cocci in pairs and chains at the microscopic examination, were included in the study. The BCs included were collected by venipuncture, were mono-microbial and were the first bottles that flagged positive in each set. Complete blood count requested simultaneously with BCs along with medical history taken by the ED physician were also evaluated.
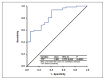
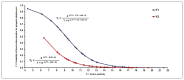
Results: In our case series, all BCs positive for Gram positive cocci in pairs or chains at microscopic examination with a TTP ≤6.3 hours were consistent with a pyogenic streptococcus (100% specificity; 95% CI: 92.7-100). Consequently, a TTP ≤6.3 hours has a 100% positive predictive value (95% CI: 30.9-100). Conversely, no pyogenic streptococci were recovered from positive BCs with a TTP >12.6 hours. Therefore, as screening test, it has 100% sensitivity (95% CI: 77-100) and 100% negative predictive value (95% CI: 83.4-100). The binomial logistic regression model showed how as TTP increases, in BCs positive for Gram positive cocci in pairs and chains at the microscopic examination, the probability of a positive result for pyogenic streptococci decreases (odds ratio: 0.548; 95% confidence interval: 0.387-0.775; P=0.001).
Conclusions: The results of this study are an adjunctive tool to clinical aspects and fast microbiology laboratory tests to help assessing the likelihood of a positive blood culture for pyogenic streptococci.
Keywords: Blood Cultures; Pyogenic streptococci; microbiology; time to positivity.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that this research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Schønheyder HC, Højbjerg T. The impact of the first notification of positive blood cultures on antibiotic therapy. A one-year survey. APMIS. 1995;103:37–44. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
