Efficacy and safety of ritlecitinib in Asian patients with alopecia areata: A subgroup analysis of the ALLEGRO phase 2b/3 trial
- PMID: 40071721
- PMCID: PMC11975179
- DOI: 10.1111/1346-8138.17539
Efficacy and safety of ritlecitinib in Asian patients with alopecia areata: A subgroup analysis of the ALLEGRO phase 2b/3 trial
Abstract
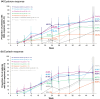
This subgroup analysis of the ALLEGRO phase 2b/3 study (NCT3732807) assessed the efficacy and safety of multiple doses of ritlecitinib, an oral JAK3/TEC family kinase inhibitor, in Asian patients with alopecia areata (AA). Patients aged ≥12 years with AA and ≥50% scalp hair loss received once-daily ritlecitinib 50 or 30 mg (with or without 4-week 200-mg loading dose ["200/50" or "200/30"]) or 10 mg or placebo for 24 weeks, followed by a 24-week extension, in which patients initially assigned to placebo switched to 200/50 or 50 mg. In this subgroup analysis, Asian patients with response based on achieving a Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) score ≤20, SALT ≤10, ≥2-grade improvement or normal score on the eyebrow assessment (EBA) scale, and ≥2-grade improvement or normal score on the eyelash assessment (ELA) scale were evaluated through week 48. Safety was monitored throughout. In total, 186 Asian patients were randomized to ritlecitinib 200/50 mg (n = 33), 200/30 mg (n = 28), 50 mg (n = 43), 30 mg (n = 34), 10 mg (n = 17), placebo to 200/50 mg (n = 14), or placebo to 50 mg (n = 17). The proportions of patients treated with ritlecitinib ≥30 mg achieving a SALT score ≤20 response were 9.1%-36.4% at week 24 vs 0% for the 10-mg group and 3.2% for placebo. At week 48, 26.5%-55.6% of patients treated with ritlecitinib ≥30 mg achieved a SALT ≤20 response. At week 48, the proportions of patients treated with ritlecitinib ≥30 mg with EBA response were 41.9%-71.1% and with ELA response were 40.7%-57.9%. The most common adverse events were nasopharyngitis, folliculitis, upper respiratory tract infection, and urticaria. No serious or opportunistic infections, major adverse cardiovascular events, thromboembolic events, malignancies, or deaths were reported. Ritlecitinib demonstrated clinical efficacy and acceptable safety over 48 weeks in Asian patients ≥12 years with AA and ≥50% hair loss. Results for the Asian subpopulation were consistent with the overall population in the ALLEGRO-2b/3 study.
Keywords: ALLEGRO; SALT; Severity of Alopecia Tool; alopecia areata; ritlecitinib.
© 2025 Pfizer Inc. and The Author(s). The Journal of Dermatology published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Dermatological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
X.Z. is a clinical trial investigator for Pfizer. Y.Y. and W.S. declare no conflicts of interest. Y. Sheng is a clinical trial investigator for Pfizer, Eli Lilly, AbbVie, Reistone Biopharma, Sanofi, Sichuan Kelun Pharmaceutical, and Suzhou Zelgen Biopharmaceuticals. M.K. is a clinical trial investigator for AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly Japan Inc., and Pfizer. O.K. is a clinical trial investigator for Eli Lilly Japan Inc. and Pfizer. C‐C.L. is a clinical investigator for Pfizer, Eli Lilly, AbbVie, Teva, Cerner Enviza, and Janssen. G.S., R.W., S.H., Q.S., Y. Shen, and M.S‐Y. are employees of and hold stock or stock options in Pfizer Inc. Taisuke Ito is a clinical trial investigator for Eli Lilly Japan I and Pfizer, and is an Editorial Board member of
Figures





References
-
- Zhang B, Zhao Y, Cai Z, Caulloo S, McElwee KJ, Li Y, et al. Early stage alopecia areata is associated with inflammation in the upper dermis and damage to the hair follicle infundibulum. Australas J Dermatol. 2013;54:184–191. - PubMed
-
- Islam N, Leung PS, Huntley AC, Gershwin ME. The autoimmune basis of alopecia areata: a comprehensive review. Autoimmun Rev. 2015;14:81–89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

