Phagocytosis-driven neurodegeneration through opposing roles of an ABC transporter in neurons and phagocytes
- PMID: 40073145
- PMCID: PMC11900885
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adr5448
Phagocytosis-driven neurodegeneration through opposing roles of an ABC transporter in neurons and phagocytes
Abstract
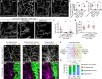
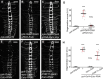
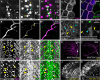
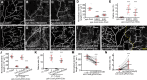
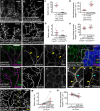
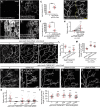
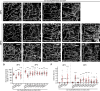
Lipid homeostasis is critical to neuronal survival. ATP-binding cassette A (ABCA) proteins are lipid transporters associated with neurodegenerative diseases. How ABCA transporters regulate lipid homeostasis in neurodegeneration is an outstanding question. Here we report that the Drosophila ABCA protein engulfment ABC transporter in the ovary (Eato) regulates phagocytosis-dependent neurodegeneration by playing opposing roles in neurons and phagocytes: In neurons, Eato prevents dendrites and axons from being attacked by neighboring phagocytes; in phagocytes, Eato sensitizes the cell for detecting neurons as engulfment targets. Thus, Eato deficiency in neurons alone causes phagocytosis-dependent neurite degeneration, but additional Eato loss from phagocytes suppresses the neurite degeneration. Mechanistically, Eato functions by removing the eat-me signal phosphatidylserine from the cell surface in both neurons and phagocytes. Multiple human and worm ABCA homologs can rescue Eato loss in phagocytes but not in neurons, suggesting both conserved and cell type-specific activities of ABCA proteins. These results imply possible mechanisms of neuron-phagocyte interactions in neurodegenerative diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Quazi F., Molday R. S., Lipid transport by mammalian ABC proteins. Essays Biochem. 50, 265–290 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Broccardo C., Luciani M.-F., Chimini G., The ABCA subclass of mammalian transporters. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1461, 395–404 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Albrecht C., Viturro E., The ABCA subfamily—gene and protein structures, functions and associated hereditary diseases. Pflugers Arch. 453, 581–589 (2007). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

