Role of oxidative balance score in staging and mortality risk of cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome: Insights from traditional and machine learning approaches
- PMID: 40073760
- PMCID: PMC11950999
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2025.103588
Role of oxidative balance score in staging and mortality risk of cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome: Insights from traditional and machine learning approaches
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate the roles of oxidative balance score (OBS) in staging and mortality risk of cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome (CKM).
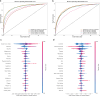
Methods: Data of this study were from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999-2018. We performed cross-sectional analyses using multinomial logistic regression to investigate the relationship between OBS and CKM staging. Cox proportional hazards models were used to assess the impact of OBS on mortality outcomes in CKM patients. Additionally, mediation analyses were performed to explore whether OBS mediated the relationships between specific predictors (Life's Simple 7 score [LS7], systemic immune-inflammation index [SII], frailty score) and mortality outcomes. Then, machine learning models were developed to classify CKM stages 3/4 and predict all-cause mortality, with SHapley Additive exPlanations values used to interpret the contribution of OBS components.
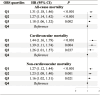
Results: 21,609 participants were included (20,319 CKM, median [IQR] age: 52.0 [38.0-65.0] years, 54.3% male, median [IQR] follow-up: 9.4 [5.3-14.1] years). Lower OBS quartiles were associated with advanced CKM staging. Moreover, lower OBS quartiles were related to increased mortality risk, compared to Q4 of OBS (all-cause mortality: Q1: HR 1.31, 95% CI 1.18-1.46, Q2: HR 1.27, 95% CI 1.14-1.42, Q3: HR 1.18, 95% CI 1.06-1.32; cardiovascular mortality: Q1: HR 1.44, 95% CI 1.16-1.79, Q2: HR 1.39, 95% CI 1.11-1.74, Q3: HR 1.26, 95% CI 1.01-1.57; non-cardiovascular mortality, Q1: HR 1.27, 95% CI 1.12-1.44, Q2: HR 1.23, 95% CI 1.08-1.40, Q3: HR 1.16, 95% CI 1.02-1.31), with optimal risk stratification threshold for OBS was 22. Additionally, OBS mediated (ranging 4.25%-32.85 %) effects of SII, LS7, frailty scores on mortality outcomes. Moreover, light gradient boosting machine achieved the highest performance for predicting advanced CKM staging (area under curve: 0.905) and all-cause mortality (area under curve: 0.875). Cotinine increased risk, while magnesium, vitamin B6, physical activity were protective.
Conclusions: This study highlights OBS as a risk stratification tool for CKM, emphasizing oxidative stress's role in CKM staging and mortality risk management.
Keywords: Cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome; Mortality; Oxidative balance score; Oxidative stress; Risk stratification.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest associated with this manuscript. All authors have no financial, personal, or professional relationships that could inappropriately influence or bias the content of this work.
Figures



References
-
- Ndumele C.E., Rangaswami J., Chow S.L., Neeland I.J., Tuttle K.R., Khan S.S., Coresh J., Mathew R.O., Baker-Smith C.M., Carnethon M.R., Despres J.-P., Ho J.E., Joseph J.J., Kernan W.N., Khera A., Kosiborod M.N., Lekavich C.L., Lewis E.F., Lo K.B., Ozkan B., Palaniappan L.P., Patel S.S., Pencina M.J., Powell-Wiley T.M., Sperling L.S., Virani S.S., Wright J.T., Rajgopal Singh R., Elkind M.S.V. Cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic health: a presidential advisory from the American heart association. Circulation. 2023;148(20):1606–1635. - PubMed
-
- Trimarco V., Izzo R., Pacella D., Virginia Manzi M., Trama U., Lembo M., Piccinocchi R., Gallo P., Esposito G., Morisco C., Rozza F., Mone P., Jankauskas S.S., Piccinocchi G., Santulli G., Trimarco B. Increased prevalence of cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome during COVID-19: a propensity score-matched study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2024;218 - PubMed
-
- Sebastian S.A., Padda I., Johal G. Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic (CKM) syndrome: a state-of-the-art review. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2024;49(2) - PubMed
-
- Sen P., Hamers J., Sittig T., Shashikadze B., d’Ambrosio L., Stöckl J.B., Bierschenk S., Zhang H., d’Alessio C., Zandbergen L.M., Pauly V., Clauss S., Wolf E., Dendorfer A., Fröhlich T., Merkus D. Oxidative stress initiates hemodynamic change in CKD-induced heart disease. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2024;119(6):957–971. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

