Development of a rapid malaria LAMP-MS assay for diagnosis of malaria infections
- PMID: 40074752
- PMCID: PMC11904186
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-92935-4
Development of a rapid malaria LAMP-MS assay for diagnosis of malaria infections
Abstract
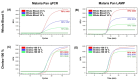
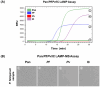
Malaria remains a critical global health concern, especially in tropical and subtropical regions, where it causes substantial morbidity and mortality. Current diagnostic methods, such as microscopy and PCR-based assays, are reliable but often impractical in resource-limited settings due to their dependency on complex equipment and skilled personnel. This study developed a novel malaria diagnostic platform by combining the Chelex-100/boiling DNA extraction method with a Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification-MicroScanner (LAMP-MS) assay. The Chelex-100/boiling method is simpler and more cost-effective than conventional DNA extraction processes, making it suitable for use in resource-limited settings. The LAMP-MS assay enables multiplex detection through a microchip design with four chambers. Each chamber of the microchip is preloaded with specific primers targeting Pan, Plasmodium falciparum (Pf), Plasmodium vivax (Pv), and an internal control, minimizing non-specific amplification in multiplex LAMP reactions. In a clinical evaluation of 260 samples, the assay demonstrated a sensitivity of 97.5% for the Pan target and 100% for the Pf-specific target in the 80 Plasmodium falciparum (Pf) clinical samples. Similarly, for the 80 Plasmodium vivax (Pv) clinical samples, the assay achieved a sensitivity of 95% for the Pan target and 94% for the Pv-specific target. Notably, in the 100 non-infected clinical samples, the assay exhibited 100% specificity, with no false positives observed. These findings suggest that LAMP-MS is a rapid and reliable alternative to PCR-based methods, especially in resource-limited environments.
Keywords: LAMP-MS; Loop-mediated isothermal amplification; Malaria; Point of care testing.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval: This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Korea University’s Guro Hospital (2021GR0337). Informed consent: Patient informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board of Korea University Guro Hospital, as the identities of the subjects were completely anonymous, and there was minimal risk involved in the study.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

