Real-World Effectiveness of Frontline Treatments Among Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Results from ConcertAI
- PMID: 40075647
- PMCID: PMC11899398
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17050799
Real-World Effectiveness of Frontline Treatments Among Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Results from ConcertAI
Abstract
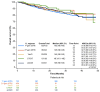
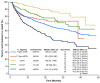
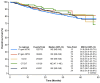
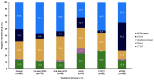
Background: The long-term follow-up of clinical trials of novel first-line (1L) therapies for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) demonstrates 6-10-year progression-free survival. We describe the effectiveness of 1L CLL treatments in real-world settings, with an emphasis on the important real-world outcome of time to next treatment or death (TTNT-D). Methods: This retrospective, observational study utilized de-identified electronic health records from the ConcertAI RWD360™ database with linked administrative open claims. Adults with CLL who initiated an approved 1L CLL therapy (June 2019-March 2023) were included. Duration of therapy (DoT), TTNT-D, and overall survival were assessed. Results: At 1L, 39.8% of 1843 patients received first-generation covalent Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors (cBTKis), 23.0% second-generation cBTKis, 12.4% venetoclax-obinutuzumab (VenO), 7.4% chemotherapy/chemoimmunotherapy (CT/CIT), and 17.4% anti-CD20 monotherapy. Median (range) follow-up in months was 24.9 (13.1-36.6) for first-generation cBTKis, 13.4 (7.3-21.7) for second-generation cBTKis, 16.0 (8.4-27.8) for VenO, 21.8 (11.2-32.7) for CT/CIT, and 19.7 (10.0-33.4) for anti-CD20 monotherapy. Median (range) DoT was 11.5 (4.2-25.0) and 8.6 (3.0-16.1), 9.1 (5.9-12.2), 5.6 (3.2-5.8), and 1.6 (1.6-4.5) months for first- and second-generation cBTKis, VenO, CT/CIT, and anti-CD20 monotherapy, respectively. Regarding TTNT-D, at 2 years' follow-up, 69.1%, 82.5%, 86.3%, 79.1%, and 53.0% of patients treated with first- and second-generation cBTKis, VenO, CT/CIT, and anti-CD20 monotherapy, respectively, had not initiated subsequent treatment or experienced death. Conclusions: TTNT-D is an important real-world outcome in CLL. Our findings demonstrated the utility of time-limited VenO, with potentially more time off treatment, relative to continuous 1L cBTKi therapies.
Keywords: chronic lymphocytic leukemia; real-world outcomes; treatment effectiveness.
Conflict of interest statement
L.E.R.: Consultant for AbbVie, Ascentage, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Janssen, Loxo Oncology, Pharmacyclics, Pfizer, and TG Therapeutics; member of a data safety monitoring committee for Ascentage; served as a CME speaker for DAVA, Curio, Medscape, and PeerView; holds minority ownership interest in Abbott Laboratories; received travel support from LOXO oncology; and received research funding (paid to the institution) from Adaptive Biotechnologies, AstraZeneca, Genentech, AbbVie, Pfizer, Loxo Oncology, Aptose Biosciences, Dren Bio, and Qilu Puget Sound Biotherapeutics. J.M.B.: Consulting or advisory role: Genentech/Roche, AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Adaptive Biotechnologies, BeiGene, Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb, Nurix, Genmab, Foresight Diagnostics, Regeneron, and Seagen; speakers’ bureau: Seagen and BeiGene; travel, accommodations, and expenses: Genentech/Roche. J.M.R.: Consultant: Verastem, AbbVie/Genentech, PCYC, and AstraZeneca. C.E.J.: Consultancy: AbbVie. M.S.: Consulting, advisory boards, steering committees, or data safety monitoring committees: AbbVie, Genentech, AstraZeneca, Genmab, Janssen, Beigene, Bristol Myers Squibb, Morphosys/Incyte, Kite Pharma, Eli Lilly, Mustang Bio, Fate Therapeutics, Nurix, and Merck; institutional research funding from Mustang Bio, Genentech, AbbVie, BeiGene, AstraZeneca, Genmab, Morphosys/Incyte, and Vincerx; stock options: Koi Biotherapeutics; employment: Bristol Myers Squibb (spouse). N.E., D.J., B.S.M., L.R., Y.L., W.S., and J.R.: Employees of AbbVie and may hold stock or stock options. S.E.M.: Retired from AbbVie.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

