Unlocking the Microbial Symphony: The Interplay of Human Microbiota in Cancer Immunotherapy Response
- PMID: 40075661
- PMCID: PMC11899421
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17050813
Unlocking the Microbial Symphony: The Interplay of Human Microbiota in Cancer Immunotherapy Response
Abstract
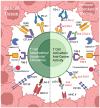
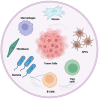
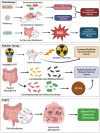
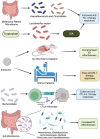
Introduction: The emergence of cancer immunotherapy has revolutionized cancer treatment, offering remarkable outcomes for patients across various malignancies. However, the heterogeneous response to immunotherapy underscores the necessity of understanding additional factors influencing treatment efficacy. Among these factors, the human microbiota has garnered significant attention for its potential role in modulating immune response. Body: This review explores the intricate relationship between the human microbiota and cancer immunotherapy, highlighting recent advances and potential mechanisms underlying microbial influence on treatment outcomes.
Conclusion: Insights into the microbiome's impact on immunotherapy response not only deepen our understanding of cancer pathogenesis but also hold promise for personalized therapeutic strategies aimed at optimizing patient outcomes.
Keywords: cancer; immunotherapy; microbiome; microbiota.
Conflict of interest statement
J.C. serves as a consultant and Immunotherapy Subject Matter Expert for Guidepoint Consulting (New York, NY, USA) and is an inventor on Patent Number(s): US20170044496A1 and received royalties for this technology license.
Figures
References
-
- Dorta-Estremera S., Hegde V.L., Slay R.B., Sun R., Yanamandra A.V., Nicholas C., Nookala S., Sierra G., Curran M.A., Sastry K.J. Targeting interferon signaling and CTLA-4 enhance the therapeutic efficacy of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in preclinical model of HPV+ oral cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer. 2019;7:252. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0728-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang B., Xu Z., Sunthamala N., Yaguchi T., Huang J., Kawakami Y., Gong Y., Tang H., Li S., Guo Y., et al. Combinatorial sympathetic and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) blockades inhibit the murine melanoma growth by targeting infiltrating T cells. Transl. Cancer Res. 2021;10:899–913. doi: 10.21037/tcr-20-2738. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

