Rheological Properties of Polyethylene Color Masterbatches Containing Pigment RED 122 (2,9-Dimethylquinacridone) Modified by Silanes Using Pulverization Method
- PMID: 40076111
- PMCID: PMC11902374
- DOI: 10.3390/polym17050618
Rheological Properties of Polyethylene Color Masterbatches Containing Pigment RED 122 (2,9-Dimethylquinacridone) Modified by Silanes Using Pulverization Method
Abstract
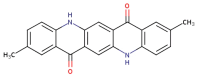
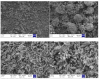
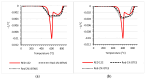
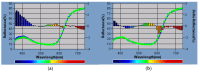
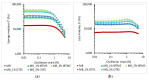
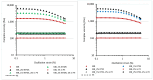
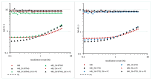
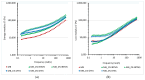
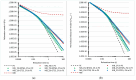
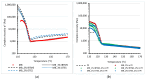
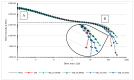
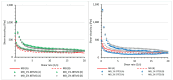
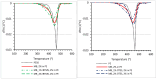
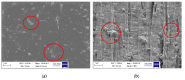
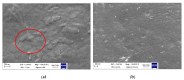
Polyethylene color masterbatches containing pigment RED 122, 2,9-dimethylquinacridone, ((2,9-dimethyl-5,12-dihydroquinolino[2,3-b]acridine-7,14-dione) modified by the pulverization method in ball mills were obtained. As pigment-modifying agents, isobutyltrimethoxysilane IBTMS and octyltrietoxysilane OTES were used. The viscoelastic properties of the prepared masterbatches were investigated by using an oscillation rotational rheometer. The impact of the 2 wt.% of coloring masterbatch on the rheological behavior of polyethylene during processing at 170 °C was analyzed. Storage shear modulus G', loss shear modulus G″, complex viscosity η* and loss factor tan δ were analyzed. Modification prevents the agglomeration of modified pigment particles in the masterbatch, leading to a significant increase in the storage shear modulus G', from 13.83 kPa (masterbatch containing pigment RED 122) to 58.74 kPa (pigment modified with 2 wt.% of IBTMS) and 49.67 kPa (pigment modified with 2 wt.% of OTES). The analysis of the continuous relaxation models showed that the modified pigment influenced the relaxation of melted polyethylene. The tendency of the silane-modified pigment to create its "own structure" in the polyethylene carrier via particle-particle interactions was estimated based on rotational tests at low and high shear rates. The larger area of viscosity loops was determined at 170 °C for the masterbatch containing 1 wt.% of OTES-modified pigment, 2574.44 Pas(1/s), as compared with the reference masterbatch, 464.88 Pas(1/s). The Carreau and Carreau-Yasuda viscosity models were applied to analyze the flow curve and the changes in viscosity as a function of the shear rate. After pigment modification, the zero shear viscosity µ0 of the mixtures of polyethylene/pigment masterbatch changed from 234.9 Pas (pigment RED 122) to 305.9 Pas (pigment modified with 1 wt.% of IBTMS). The influence of the modified pigments on the crystallization of polyethylene and its thermal stability was investigated. The temperatures of melting Tm were determined.
Keywords: polyethylene masterbatches; quinacridone pigments; viscoelastic properties.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
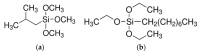

Similar articles
-
Polypropylene Color Masterbatches Containing Layered Double Hydroxide Modified with Quinacridone and Phthalocyanine Pigments-Rheological, Thermal and Application Properties.Materials (Basel). 2023 Sep 16;16(18):6243. doi: 10.3390/ma16186243. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37763521 Free PMC article.
-
Rheological properties of resin composites according to variations in monomer and filler composition.Dent Mater. 2006 Jun;22(6):515-26. doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2005.05.008. Epub 2005 Sep 19. Dent Mater. 2006. PMID: 16171856
-
Influence of Compounding Parameters on Color Space and Properties of Thermoplastics with Ultramarine Blue Pigment.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Dec 15;15(24):4718. doi: 10.3390/polym15244718. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38139970 Free PMC article.
-
Rheological stability of carbomer in hydroalcoholic gels: Influence of alcohol type.Int J Cosmet Sci. 2021 Dec;43(6):748-763. doi: 10.1111/ics.12750. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2021. PMID: 34741768
-
Effect of Temperature and Alkali Solution to Activate Diethyl Carbonate for Improving Rheological Properties of Modified Hydroxyethyl Methyl Cellulose.ACS Omega. 2024 Jan 18;9(4):4540-4554. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c07451. eCollection 2024 Jan 30. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38313537 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Witucki G.L. Silane Primer: Chemistry and Applications of AIkoxy Silanes. J. Coat. Technol. 1993;65:57–60.
-
- Deschler U., Kleinschmit P., Panster P. 3-Chloropropyltrialkoxy Silanes—Key Intermediates for the Commercial Production of Organofunctionalized Silanes and Polysiloxanes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1986;25:236–252. doi: 10.1002/anie.198602361. - DOI
-
- Zhu D., Hu N., Schaefer D.W. Water-based sol–gel coatings for military coating applications, chapter 1. In: Zarras P., Soucek M.D., Atul Tiwari A., editors. Handbook of Waterborne Coatings. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2020. pp. 1–27. - DOI
-
- Wang D., Ren F., Zhu C., Feng J., Cheng Q., Chen S., Shen G., Wang F. Hybrid silane technology in silica-reinforced tread compound. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2019;92:310–325. doi: 10.5254/rct.18.81563. - DOI
-
- Máková V., Holubová B., Krabicová I., Kulhánková J., Řezanka M. Hybrid organosilane fibrous materials and their contribution to modern science. Polymer. 2021;228:123862. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2021.123862. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

