Self-Toughened Epoxy Resin via Hybridization of Structural Isomeric Curing Agents
- PMID: 40076187
- PMCID: PMC11902468
- DOI: 10.3390/polym17050695
Self-Toughened Epoxy Resin via Hybridization of Structural Isomeric Curing Agents
Abstract
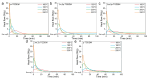
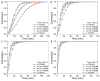
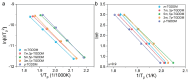
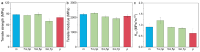
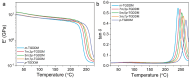
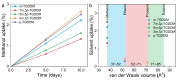
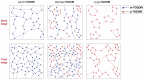
Fracture toughness is a key property of epoxy resins with a high glass transition temperature (Tg), used in carbon fiber/epoxy composites for aerospace applications. Conventional toughening methods rely on adding toughening agents, often compromising the processibility and thermal stability. This study introduces a simple self-toughening approach that enhances the fracture toughness without sacrificing other properties by controlling the cured epoxy network structure. Tetraglycidyl 4,4'-diaminodiphenylmethane (TGDDM) epoxy resin was cured using mixtures of structural isomeric curing agents, 3,3'- and 4,4'-diaminodiphenyl sulfone (3,3'- and 4,4'-DDS), at ratios of 7:3, 5:5, and 3:7. The optimal 7:3 ratio produced a resin with 30% higher fracture toughness compared to TGDDM/3,3'-DDS and 100% higher than the TGDDM/4,4'-DDS system. The Tg of the self-toughened resin ranged from 241 to 266 °C, which was intermediate between the Tg values of the TGDDM/3,3'-DDS and TGDDM/4,4'-DDS systems. This improvement is attributed to the higher crosslink density and reduced free volume of the epoxy network. These findings demonstrate that simply mixing isomeric curing agents enables self-toughening, providing a practical and efficient strategy to enhance the performance of high-Tg epoxy resins in advanced composite applications.
Keywords: curing agent; diaminodiphenyl sulfone; epoxy resin; fracture toughness; structural isomers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Le Q.-H., Kuan H.-C., Dai J.-B., Zaman I., Luong L., Ma J. Structure–property relations of 55 nm particle-toughened epoxy. Polymer. 2010;51:4867–4879. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2010.08.038. - DOI
-
- Stutz H. Lifetime assessment of epoxies by the kinetics of thermal degradation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004;91:1881–1886. doi: 10.1002/app.13240. - DOI
-
- Carra G., Carvelli V. Ageing of pultruded glass fibre reinforced polymer composites exposed to combined environmental agents. Compos. Struct. 2014;108:1019–1026. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2013.10.042. - DOI
-
- Johnsen B., Kinloch A., Taylor A. Toughness of syndiotactic polystyrene/epoxy polymer blends: Microstructure and toughening mechanisms. Polymer. 2005;46:7352–7369. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2005.05.151. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

