Vitamin K Properties in Stroke and Alzheimer's Disease: A Janus Bifrons in Protection and Prevention
- PMID: 40076254
- PMCID: PMC11901974
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30051027
Vitamin K Properties in Stroke and Alzheimer's Disease: A Janus Bifrons in Protection and Prevention
Abstract
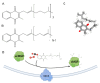
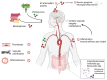
Vitamin K is essential for many physiological processes, including coagulation, bone metabolism, tissue calcification, and antioxidant activity. Vitamin K vitamers are represented by lipophilic compounds with similar chemical structure (i.e., phylloquinone (vitamin K1) and menaquinone (vitamin K2)). Vitamin K deficiency can affect coagulation and vascular calcification, increasing the risk of hemorrhages, atherosclerosis, cerebrovascular diseases, and neurodegeneration. Recently, several studies have hypothesized a possible dual role of vitamin K vitamers in benefiting both vascular and cerebral health, e.g., by sphingolipids biosynthesis or ferroptosis inhibition. The aim of this narrative review is to deepen the understanding of biological activities of vitamin K and its possible dual protective/preventive actions in neurovascular and degenerative conditions, e.g., stroke and dementia. Given the difficulties related to hemorrhagic risk entailed in the prevention of strokes, the function of vitamin K antagonists is also investigated. Finally, we track the development of a clinical concept for a future preventive strategy and innovative use of vitamin K as a supplement to counteract neurovascular and pathological processes, focusing in particular on stroke and dementia.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; amyloid B; biological activity; coagulation; neurodegeneration; stroke; vascular calcification; vitamin K.
Conflict of interest statement
D.D.A., G.S., L.G. and R.A.C. declare no conflicts of Interest. A.F. is a consultant to Gnosys by Lesaffre.
Figures
References
-
- Ulrich M.M., Furie B., Jacobs M.R., Vermeer C., Furie B.C. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation. A synthetic peptide based upon the gamma-carboxylation recognition site sequence of the prothrombin propeptide is an active substrate for the carboxylase in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 1988;263:9697–9702. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(19)81574-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mladěnka P., Macáková K., Kujovská Krčmová L., Javorská L., Mrštná K., Carazo A., Protti M., Remião F., Nováková L., OEMONOM Researchers and Collaborators Vitamin K—Sources, physiological role, kinetics, deficiency, detection, therapeutic use, and toxicity. Nutr. Rev. 2022;80:677–698. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuab061. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

