Animal Model Screening for Hyperlipidemic ICR Mice
- PMID: 40076768
- PMCID: PMC11900507
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26052142
Animal Model Screening for Hyperlipidemic ICR Mice
Abstract
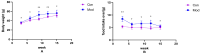
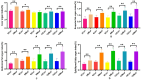
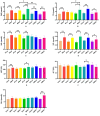
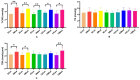
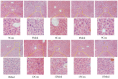
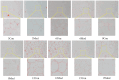
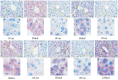
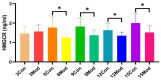
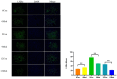
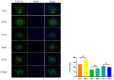
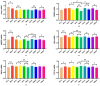
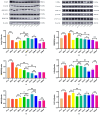
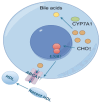
This study aimed to establish a hyperlipidemia model in ICR mice using a homemade high-fat diet. It further investigated hyperlipidemia-related indicators in control and model mice at various feeding durations to determine the optimal time frame for successful model establishment. Sixteen male ICR mice were introduced at intervals of 3 weeks, starting from weeks 0, 3, 6, 9, and 12. The control group was fed a standard diet, while the model group received a homemade high-fat diet to induce hyperlipidemia. Blood lipid related indices were detected at 15 weeks. The liver, scapular fat, abdominal fat, and epididymal fat were harvested to calculate the organ index. The contents of T-CHO, TG, and TBA in the liver were measured. HE staining was used to observe pathological changes in liver tissue and white adipose tissue, while Oil Red O staining was used to observe lipid droplets in liver tissue. The mRNA and protein expression of SREBP-2, insig1, HMGCR, LXRα, ABCA1, and CYP7A1 in the liver were detected by RT-qPCR and Western Blot. In the model group, blood lipid levels significantly increased by the 9th week, aligning with pathological changes indicative of hyperlipidemia. The mRNA and protein expression levels of SREBP-2, Insig-1, HMGCR, LXRα, ABCA1, and CYP7A1 were markedly elevated at 9 weeks and remained relatively stable thereafter. This study provides a reliable reference for determining the optimal establishment time of hyperlipidemia models and for in vivo hyperlipidemia animal experiments.
Keywords: HMGCR; cholesterol reverse transport; cholesterol synthesis; hyperlipidemia; model screening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
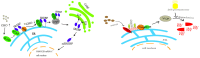

Similar articles
-
[Effect of electroacupuncture at "Fenglong" (ST 40) on liver cholesterol metabolism in hyperlipidemia rats based on AMPK/mTOR pathway].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2024 Oct 12;44(10):1155-64. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20231011-k0002. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2024. PMID: 39401813 Chinese.
-
The fucoidan A3 from the seaweed Ascophyllum nodosum enhances RCT-related genes expression in hyperlipidemic C57BL/6J mice.Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Aug 1;134:759-769. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.070. Epub 2019 May 14. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019. PMID: 31100394
-
[Study on anti-hyperlipidemia effect of Linderae Radix via regulating reverse cholesterol transport].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Apr;46(7):1795-1802. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200104.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 33982484 Chinese.
-
[Fresh Rehmanniae Radix regulates cholesterol metabolism disorder in mice fed with high-fat and high-cholesterol diet via FXR-mediated bile acid reabsorption].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025 Mar;50(6):1670-1679. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20241123.302. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40350954 Chinese.
-
Effects of oral selenium and magnesium co-supplementation on lipid metabolism, antioxidative status, histopathological lesions, and related gene expression in rats fed a high-fat diet.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Jul 21;17(1):165. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0815-4. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 30031400 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang Y., Chen J., Zhang Y., Li S., Wang Y., Zhang Y., Shi C. Mechanism of Total Saponin of Astragali Radix and Total Alkaloids of Nelumbinis Folium Against Hyperlipidemia Based on PPARγ/LXRα/ABCG1 Signaling Pathway. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae. 2024;30:37–44. doi: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20240243. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

