Circ_0011446 Regulates Intramuscular Adipocyte Differentiation in Goats via the miR-27a-5p/FAM49B Axis
- PMID: 40076914
- PMCID: PMC11900246
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26052294
Circ_0011446 Regulates Intramuscular Adipocyte Differentiation in Goats via the miR-27a-5p/FAM49B Axis
Abstract
Intramuscular fat (IMF), or marbling, is a critical indicator of goat meat quality. Non-coding RNAs play a key role in the formation and deposition of IMF in vertebrates by regulating genes involved in its synthesis, degradation, and transport. The competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) hypothesis identifies circular RNAs (circRNAs) as natural "sponges" for microRNAs (miRNAs). However, the precise mechanisms of circRNAs in goat IMF remain poorly understood. In the current study, we utilized existing sequencing data to construct a ceRNA regulatory network associated with intramuscular adipogenesis and fat deposition in goats. Our goal was to elucidate the post-transcriptional regulatory mechanism of family with sequence similarity 49 member B (FAM49B). Functionally, FAM49B was found to inhibit the differentiation of intramuscular preadipocytes and to directly interact with miR-27a-5p. Mechanistically, dual-luciferase reporter assays and quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) confirmed the interaction between circ0011446 and miR-27a-5p. Circ0011446 enhanced the expression of FAM49B mRNA and protein through post-transcriptional regulation. As a ceRNA, circ0011446 competitively binds miR-27a-5p, preventing miR-27a-5p from degrading FAM49B. In conclusion, our findings demonstrate that circ0011446 suppresses goat adipogenic differentiation of intramuscular preadipocytes by regulating the expression of the downstream target gene FAM49B through miR-27a-5p sequestration. This study provides a reference for goat meat quality or livestock breeding.
Keywords: FAM49B; circ_0011446; goat; intramuscular adipocyte differentiation; miR-27a-5p.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
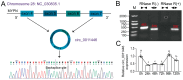
 and
and  represent the convergent prime and divergent prime, respectively. (C). Relative circ_0011446 expression during goat intramuscular adipocyte differentiation. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between groups according to one-way ANOVA (p < 0.01).
represent the convergent prime and divergent prime, respectively. (C). Relative circ_0011446 expression during goat intramuscular adipocyte differentiation. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between groups according to one-way ANOVA (p < 0.01).



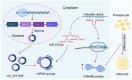
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

