Synergistic Neuroprotection Through Epigenetic Modulation by Combined Curcumin-Enriched Turmeric Extract and L-Ascorbic Acid in Oxidative Stress-Induced SH-SY5Y Cell Damage
- PMID: 40077595
- PMCID: PMC11898916
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14050892
Synergistic Neuroprotection Through Epigenetic Modulation by Combined Curcumin-Enriched Turmeric Extract and L-Ascorbic Acid in Oxidative Stress-Induced SH-SY5Y Cell Damage
Abstract
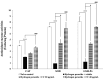
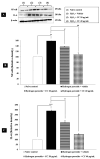
Epigenetic modulation plays a crucial role in neuroprotection by regulating cellular responses to stress, inflammation, and oxidative damage, particularly in neurodegenerative diseases. Recognizing the therapeutic potential of epigenetic regulators, this study investigated the synergistic neuroprotective effects of curcumin-enriched turmeric extract combined with L-ascorbic acid, focusing on its modulation of epigenetic pathways in oxidative stress-induced neuronal damage. SH-SY5Y neuronal cells were treated with the combination at 20 and 40 µg/mL, and subsequently exposed to 200 µM hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to induce oxidative stress. Cell viability was assessed using the MTT assay, while neuroprotective mechanisms were evaluated by analyzing the markers of epigenetic modulation, oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. The combination significantly enhanced cell viability, upregulated sirtuin-1 (SIRT1), and reduced DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) expression, indicating effective epigenetic modulation. Enhanced antioxidant defenses were observed, as evidenced by increased activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), along with decreased malondialdehyde (MDA) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, alleviating oxidative stress. Additionally, it suppressed nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) activity and its downstream mediator interleukin-6 (IL-6), thereby mitigating inflammation. The treatment also increased anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 expression while reducing pro-apoptotic markers, including caspase-3 and caspase-9, suggesting inhibition of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway. These findings highlight the novel neuroprotective effects of this combination, demonstrating its ability to modulate epigenetic pathways while reducing oxidative stress, suppressing inflammation, and preventing undesired apoptosis. Its multifaceted neuroprotective properties make it a promising functional ingredient in functional foods for neurodegenerative disease intervention. However, further investigations, including animal studies and clinical trials, are essential to evaluate its safety and therapeutic potential.
Keywords: L-ascorbic acid; curcumin; epigenetics; neurodegenerative diseases; turmeric.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Wen K.-X., Miliç J., El-Khodor B., Dhana K., Nano J., Pulido T., Kraja B., Zaciragic A., Bramer W.M., Troup J., et al. The Role of DNA Methylation and Histone Modifications in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0167201. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167201. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

