The relationship between interpersonal security and social media dependence: a moderated mediation model
- PMID: 40078527
- PMCID: PMC11897796
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1536539
The relationship between interpersonal security and social media dependence: a moderated mediation model
Abstract
Background: Interpersonal security is an important psychological factor influencing social media use. However, little is known about the mediating and moderating mechanisms linking Interpersonal security and social media dependence.
Objective: The present study explored the mediating role of negative rumination between interpersonal safety and social media dependence, as well as cohort differences in sibling conditions as moderators.
Methods: A total of 986 college students were surveyed using a cross-sectional design. Participants completed the Interpersonal Security Questionnaire, the Social Media Dependence Scale, and the Negative Rumination Scale.
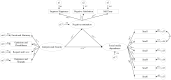
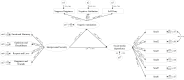
Results: The results showed that a significant interrelationship between interpersonal security, negative rumination, and social media dependence. In addition, the role of negative rumination as a mediator of interpersonal security and social media dependence was supported, and the mediating effects were different between the only-child and non-only-child cohorts.
Conclusions: Findings of the study provide a psychological basis for the treatment of social media dependence behavior in college students, with the aim of increasing their interpersonal security and reducing their dependence on social media.
Keywords: college students; interpersonal security; negative rumination; sibling condition; social media dependence.
Copyright © 2025 Li, Tan, Zhang, Wang and Yi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Keles B, McCrae N, Grealish A. A systematic review: the influence of social media on depression, anxiety and psychological distress in adolescents. Int J Adolescence Youth. (2020) 25:79–93. doi: 10.1080/02673843.2019.1590851 - DOI
-
- Li L, Niu Z, Mei S, Griffiths MD. A network analysis approach to the relationship between fear of missing out (FoMO), smartphone addiction, and social networking site use among a sample of Chinese university students. Comput Hum Behav. (2022) 128:107086. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2021.107086 - DOI
-
- Neophytou E, Manwell LA, Eikelboom R. Effects of excessive screen time on neurodevelopment, learning, memory, mental health, and neurodegeneration: a scoping review. Int J Ment Health Addict. (2021) 19:724–44. doi: 10.1007/s11469-019-00182-2 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

