Bruton tyrosine kinase covalent inhibition shapes the immune microenvironment in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- PMID: 40079085
- PMCID: PMC12358782
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2024.286663
Bruton tyrosine kinase covalent inhibition shapes the immune microenvironment in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Abstract
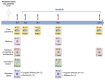
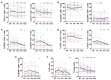
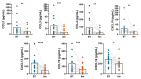
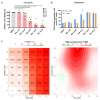
Continuous treatment with ibrutinib not only exerts tumor control but also enhances T-cell function in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). We conducted longitudinal multi-omics analyses in samples from CLL patients receiving ibrutinib upfront to identify potential adaptive mechanisms to Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibition during the first 12 months of continuous therapy. We found that ibrutinib induced a decrease in the expression of exhaustion markers and the proportion of regulatory T cells and T-follicular helper cells normalized to levels observed in healthy donors. Functionally, the expression of genes related to activation, proliferation, differentiation, and metabolism were downregulated in T cells; after in vitro stimulation, proliferation capacity was only slightly modified by ibrutinib treatment, while cytokine production was increased. In CLL cells, we observed a downregulation of immunosuppression, adhesion, and migration proteins. Adaptation at molecular level, characterized by an increase in cancer cell fraction of CLL cells with mutated driver genes, was observed in around half of the patients and was associated with retained migrative capacity towards CXCL12/CXCR4 axis. Interestingly, BTK C481S mutations were detected as early as after 6 months of treatment, particularly enriched in subsets of malignant cells retaining migrative capacity. These CLL cells with potential migrative capacity under ibrutinib also exhibited a distinct transcriptomic profile including upregulation of mTOR-AKT and MYC pathways. We identified the high expression of TMBIM6 as a potential novel independent poor prognostic factor. Of note, BIA, a TMBIM6 antagonist, induced CLL cell apoptosis and synergized with ibrutinib. In summary, our comprehensive multi-omics analysis of CLL patients undergoing ibrutinib therapy has unveiled early immunomodulatory effects on T cells and adaptative mechanisms in CLL cells. These findings can contribute to the identification of resistance mechanisms and the discovery of novel therapeutic targets.
Figures




References
-
- de Rooij MFM, Kuil A, Geest CR, et al. The clinically active BTK inhibitor PCI-32765 targets B-cell receptor–and chemokine-controlled adhesion and migration in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2012;119(11):2590-2594. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

