Real-world comparison of lisocabtagene maraleucel and axicabtagene ciloleucel in large B-cell lymphoma: an inverse probability of treatment weighting analysis with 3-year follow-up
- PMID: 40079097
- PMCID: PMC12399936
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2024.287010
Real-world comparison of lisocabtagene maraleucel and axicabtagene ciloleucel in large B-cell lymphoma: an inverse probability of treatment weighting analysis with 3-year follow-up
Abstract
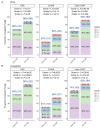
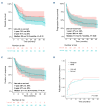
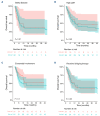
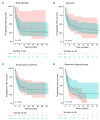
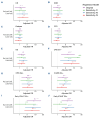
Lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) and axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel) are Food and Drug Administration- and European Medicines Agency-approved chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies for relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL). However, comparative real-world analyses of their efficacy and toxicity with extended follow-up are lacking. We conducted a retrospective study of 160 LBCL patients treated at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center with commercial liso- cel or axi-cel per standard of care. Using inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) to mitigate treatment allocation bias and multivariable adjustments to minimize other sources of confounding, we assessed the impact of CAR T-cell product type on outcomes. Axi-cel was associated with significantly higher rates of cytokine release syndrome (CRS; grade [G]1+: adjusted odds ratio [aOR] =4.27; P=0.004; G2+: aOR=2.88; P=0.006), immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS; G1+: aOR=2.10; P=0.048), and immune effector cell-associated hematotoxicity (ICAHT; G1+: aOR=8.09; P<0.001; G2+: aOR=3.86; P=0.001). Axi-cel was also associated with more frequent use of supportive care measures, such as tocilizumab (aOR=2.50; P=0.017), dexamethasone (aOR=2.77; P=0.007), and cefepime (aOR=3.37; P=0.001). We could not confirm statistically significant differences in the response rates and survival outcomes after liso-cel versus axi-cel (complete response: aOR=1.12; P=0.8; overall survival: adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] =1.34; P=0.3; progression-free survival: aHR=0.97; P=0.9; duration of response: aHR=0.89; P=0.7; cumulative incidence of relapse: aHR=0.92; P=0.8). In summary, although axicel was associated with greater toxicity requiring more intensive management, the response rates and survival outcomes were comparable between axi-cel and liso-cel.
Figures
References
-
- Locke FL, Miklos DB, Jacobson CA, et al. Axicabtagene ciloleucel as second-line therapy for large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(7):640-654. - PubMed
-
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Juno Therapeutics Inc., a Bristol-Myers Squibb Company. Breyanzi (lisocabtagene maraleucel) [package insert]. Santa Bothell, WA. https://www.fda.gov/media/145711/download. Accessed March 4, 2025.
-
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Kite Pharma, Inc. Yescarta (axicabtagene ciloleucel) [package insert]. Santa Monica, CA. https://www.fda.gov/media/108377/download. Accessed March 4, 2025.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

