Safety and effectiveness of ixekizumab in Japanese patients with psoriasis vulgaris, psoriatic arthritis, generalized pustular psoriasis, and erythrodermic psoriasis: Post-marketing surveillance
- PMID: 40079483
- PMCID: PMC12056272
- DOI: 10.1111/1346-8138.17695
Safety and effectiveness of ixekizumab in Japanese patients with psoriasis vulgaris, psoriatic arthritis, generalized pustular psoriasis, and erythrodermic psoriasis: Post-marketing surveillance
Erratum in
-
Correction to "Safety and Effectiveness of Ixekizumab in Japanese Patients with Psoriasis Vulgaris, Psoriatic Arthritis, Generalized Pustular Psoriasis, and Erythrodermic Psoriasis: Post-marketing Surveillance".J Dermatol. 2025 Nov;52(11):1753-1757. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.17976. Epub 2025 Oct 13. J Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 41084206 No abstract available.
Abstract
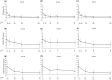
We report findings from a post-marketing study conducted from November 2016 to September 2022, which evaluated the safety and effectiveness of ixekizumab in Japanese patients with psoriasis under routine clinical practice for up to 52 weeks, and the incidence of serious infections and malignancies for up to 3 years. Of 804 patients in this analysis (67.9% male; median age, 54 years; mean disease duration, 11.8 years), 72.9%, 37.7%, 7.8%, and 3.7% had psoriasis vulgaris, psoriatic arthritis, pustular psoriasis, and erythrodermic psoriasis, respectively (subtypes not mutually exclusive). At 52 weeks, adverse events were reported in 203 patients (25.3%). Serious adverse events were reported in 36 patients (4.5%), including serious infections and infestations (n = 13, 1.6%). The incidence of serious infections and benign, malignant, and unspecified neoplasms was 0.8% (n = 5) and 0.6% (n = 4) respectively, at 3 years. Overall, 137 patients (17.0%) received Q2/Q2 treatment (160 mg starting dose, followed by 80 mg every 2 weeks from week 12); 550 patients (68.4%) received Q2/Q4 treatment (160 mg starting dose, followed by 80 mg every 2 weeks from weeks 2 to 12 and 80 mg every 4 weeks thereafter); and 117 patients (14.6%) discontinued before week 12 or received only one dose after week 12. A higher proportion of patients in the Q2/Q2 group had psoriatic arthritis (56.9% [n = 78]) compared with the Q2/Q4 group (32.9% [n = 181]). Among patients in the Q2/Q2 versus the Q2/Q4 dose groups, 21 (15.3%) and 141 (25.6%) respectively had adverse events and 2 (1.5%) and 32 (5.8%) respectively had serious adverse events. The mean Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score and body surface area percentage significantly decreased from baseline to week 52 for all psoriasis subtypes and by Q2/Q2 and Q2/Q4 ixekizumab doses (p < 0.01 or p < 0.001). Overall, the safety and effectiveness of ixekizumab in real-world settings in Japan were similar to those reported in clinical trials.
Keywords: ixekizumab; post‐marketing; psoriasis; safety; treatment effectiveness.
© 2025 The Author(s). The Journal of Dermatology published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Dermatological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Hideshi Torii has received consulting fees and/or speaker's fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly and Company, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, Maruho Co., Ltd., Novartis, Sun Pharma, and UCB Japan. Akimichi Morita has received research grants, consultancy fees, and/or speaker's fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, LEO Pharma, Maruho Co., Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Nippon Kayaku, Novartis, Pfizer Japan, Sun Pharma Japan Ltd., Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Torii Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., UCB Japan, and Ushio. Chie Yamamoto, Jiayi Dong, Mika Tsujimoto, Takashi Matsuo, and Hitoe Torisu‐Itakura are full‐time employees of Eli Lilly Japan K.K. Chie Yamamoto, Mika Tsujimoto, Takashi Matsuo, and Hitoe Torisu‐Itakura are stockholders of Eli Lilly and Company. Mamitaro Ohtsuki has received research grants and/or personal fees from AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, Eli Lilly and Company, Janssen, LEO Pharma K.K., Maruho Co., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Novartis, Taiho Pharmaceutical, and Torii Pharmaceutical. Hidehisa Saeki has received grants or contracts from AbbVie GK, Eisai Co., Ltd., LEO Pharma K.K., Maruho Co., Ltd., Sun Pharma Japan Ltd., Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Torii Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and honoraria for lectures from AbbVie GK, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly Japan K.K., LEO Pharma K.K., Maruho Co., Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis Pharma K.K., Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Torii Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and UCB Japan.
Hidehisa Saeki is an Editorial Board member of
Figures




References
-
- Ohara Y, Kishimoto M, Takizawa N, Yoshida K, Okada M, Eto H, et al. Prevalence and clinical characteristics of psoriatic arthritis in Japan. J Rheumatol. 2015;42:1439–1442. - PubMed
-
- Fujita H, Terui T, Hayama K, Akiyama M, Ikeda S, Mabuchi T, et al. Japanese dermatological association guidelines development Committee for the Guidelines for the management and treatment of generalized pustular psoriasis. Japanese guidelines for the management and treatment of generalized pustular psoriasis: the new pathogenesis and treatment of GPP. J Dermatol. 2018;45:1235–1270. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

