Incidental Brain Metastases From Prostate Cancer Diagnosed With PSMA PET/CT and MRI: A Case Series and Literature Review
- PMID: 40079497
- PMCID: PMC12068031
- DOI: 10.1002/pros.24890
Incidental Brain Metastases From Prostate Cancer Diagnosed With PSMA PET/CT and MRI: A Case Series and Literature Review
Abstract
Background: Brain metastases (BMETS) from prostate cancer are rare. Hence, brain imaging in neurologically asymptomatic patients with advanced prostate cancer (aPC) is not routinely performed. Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) PET/CT uses a radiotracer that binds to prostate cancer epithelial cells and is FDA-approved for initial staging for high-risk prostate cancer, detecting prostate cancer recurrence, and determining eligibility for radionuclide therapy.
Methods: We report six patients with asymptomatic BMETS from aPC found on staging PSMA PET/CT or MRI. Along with cranial MRI, PSMA PET/CT may be useful for detecting asymptomatic intracranial metastasis in select patients with prostate cancer.
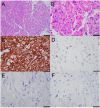
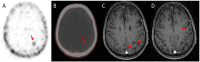
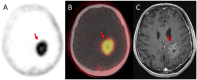
Results: Brain metastases were diagnosed in four patients by staging PSMA PET/CT scan-three after systemic disease progression and one during routine surveillance. In two other patients, BMETS were detected using MRI despite negative PSMA PET/CT for brain lesions. All were neurologically asymptomatic. Three patients had undetectable serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) concentrations; one had neuroendocrine differentiation on histology.
Conclusion: In patients with poorly differentiated or neuroendocrine aPC, BMETS may occur without neurologic symptoms and stable PSA. PSMA PET/CT may complement brain MRI for identifying BMETS in these patients.
Keywords: MRI; PET/CT; PSMA; brain metastasis; prostate cancer.
© 2025 The Author(s). The Prostate published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

