Factors affecting the impact of COVID-19 vaccination on post COVID-19 conditions among adults: A systematic literature review
- PMID: 40079963
- PMCID: PMC11913386
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2025.2474772
Factors affecting the impact of COVID-19 vaccination on post COVID-19 conditions among adults: A systematic literature review
Abstract
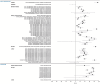
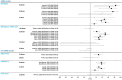
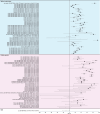
This systematic literature review summarizes the evidence across 56 publications and pre-prints (January 2020-July 2023) with low-risk of bias based on JBI critical appraisal, that report adjusted estimates for the relationship between COVID-19 vaccination and Post-COVID-19 Condition (PCC) by timing of vaccination relative to infection or PCC-onset. Comparisons of adjusted vaccine effectiveness (aVE) against ≥1 PCC (vs. unvaccinated) across study characteristics known to impact PCC burden or VE against other COVID-19 endpoints were possible for 31 studies where vaccination preceded infection. Seventy-seven percent of pre-infection aVE estimates were statistically significant (range: 7%-95%). Statistically significant pre-infection aVE estimates were slightly higher for mRNA (range: 14%-84%) than non-mRNA vaccines (range: 16%-38%) and aVE ranges before and during Omicron overlapped. Our findings suggest that COVID-19 vaccination before SARS-CoV-2 infection reduces the risk of PCC regardless of vaccine type, number of doses received, PCC definition, predominant variant, and severity of acute infections included.
Keywords: COVID-19 vaccine; Post-COVID conditions; SARS-CoV-2; long COVID; post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection; vaccine effectiveness.
Conflict of interest statement
Nadine Al Akoury, Moe H. Kyaw, Abby E. Rudolph, Julia Spinardi, John M. McLaughlin, and Hammam Haridy are employees of Pfizer Inc. and may hold stock or stock options. Kristen Markus, Isabelle Whittle, and Olivia Wright are employees of Adelphi Values PROVE™. Adelphi Values PROVE™ received funding from the study sponsor for the conduct of the review
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization . WHO COVID-19 dashboard: number of COVID-19 cases reported to WHO 2024 [accessed 2024 Sep 11]. https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/cases?n=c.
-
- Yang J, Markus K, Andersen KM, Rudolph AE, McGrath LJ, Nguyen JL, Kyaw MH, Whittle I, Blazos V, Heron L, et al. Definition and measurement of post-COVID-19 conditions in real-world practice: a global systematic literature review. BMJ Open. 2024;14(1):e077886. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2023-077886. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- National Academies of Sciences E, Medicine . A long COVID definition: a chronic, systemic disease state with profound consequences. 2024. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
