Carotid artery dissection and neurological complications after surgery for type 1 aortic dissection
- PMID: 40081929
- PMCID: PMC11907077
- DOI: 10.1136/openhrt-2024-002882
Carotid artery dissection and neurological complications after surgery for type 1 aortic dissection
Abstract
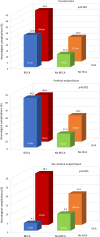
Background: Data on the prognostic impact of type A aortic dissection involving the common carotid arteries (CCAs) are scarce.
Methods: Data on the status of the CCAs were available in 1106 patients who underwent surgery for acute DeBakey type 1 aortic dissection who were recruited in a retrospective, multicentre European registry, that is, the ERTAAD. Postoperative neurological complications were defined as ischaemic stroke, haemorrhagic stroke and/or global brain ischaemia.
Results: Patients without carotid artery dissection, those with unilateral or bilateral CCA dissection had in-hospital mortality rates of 19.5%, 16.9% (OR 1.006, 95% CI 0.614 to 1.647) and 27.3% (p<0.001, OR 1.719, 95% CI 1.086 to 2.722), respectively. Bilateral, but not unilateral, dissection of the CCAs increased the risk of neurological complications (40.0% vs 18.9%, OR 2.453, 95% CI 1.683 to 3.576). The negative prognostic effect of bilateral dissection of the CCAs was increased among patients without cerebral malperfusion who underwent surgery with the use of hypothermic circulatory arrest (28.7% vs 4.3%, p=0.014).
Conclusions: Bilateral, but not unilateral, dissection of the CCAs may increase the risk of neurological complications and in-hospital mortality after surgery for DeBakey type 1 aortic dissection.
Trial registration number: NCT04831073.
Keywords: Aneurysm, Dissecting; Cardiac Surgical Procedures; Carotid Artery Diseases; STROKE.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
