Interleukin-12 signaling drives Alzheimer's disease pathology through disrupting neuronal and oligodendrocyte homeostasis
- PMID: 40082619
- PMCID: PMC12003168
- DOI: 10.1038/s43587-025-00816-2
Interleukin-12 signaling drives Alzheimer's disease pathology through disrupting neuronal and oligodendrocyte homeostasis
Abstract
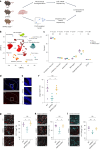
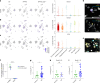
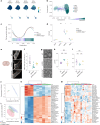
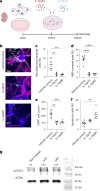
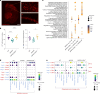
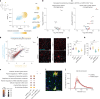
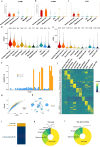
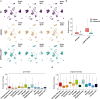
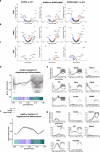
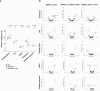
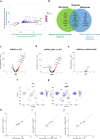
Neuroinflammation including interleukin (IL)-12/IL-23-signaling is central to Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathology. Inhibition of p40, a subunit of IL-12/IL-23, attenuates pathology in AD-like mice; however, its signaling mechanism and expression pattern remained elusive. Here we show that IL-12 receptors are predominantly expressed in neurons and oligodendrocytes in AD-like APPPS1 mice and in patients with AD, whereas IL-23 receptor transcripts are barely detectable. Consistently, deletion of the IL-12 receptor in neuroectodermal cells ameliorated AD pathology in APPPS1 mice, whereas removal of IL-23 receptors had no effect. Genetic ablation of IL-12 signaling alone reverted the loss of mature oligodendrocytes, restored myelin homeostasis, rescued the amyloid-β-dependent reduction of parvalbumin-positive interneurons and restored phagocytosis-related changes in microglia of APPPS1 mice. Furthermore, IL-12 protein expression was increased in human AD brains compared to healthy age-matched controls, and human oligodendrocyte-like cells responded profoundly to IL-12 stimulation. We conclude that oligodendroglial and neuronal IL-12 signaling, but not IL-23 signaling, are key in orchestrating AD-related neuroimmune crosstalk and that IL-12 represents an attractive therapeutic target in AD.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Guerreiro, R. J. et al. Peripheral inflammatory cytokines as biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neurodegener. Dis.4, 406–412 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Heinzel, F. P., Hujer, A. M., Ahmed, F. N. & Rerko, R. M. In vivo production and function of IL-12 p40 homodimers. J. Immunol.158, 4381–4388 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Gately, M. K. et al. The interleukin-12/interleukin-12-receptor system: role in normal and pathologic immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol.16, 495–521 (1998). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

