An asymmetric nautilus-like HflK/C assembly controls FtsH proteolysis of membrane proteins
- PMID: 40082723
- PMCID: PMC12048511
- DOI: 10.1038/s44318-025-00408-1
An asymmetric nautilus-like HflK/C assembly controls FtsH proteolysis of membrane proteins
Abstract
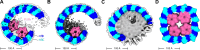
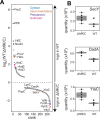
The AAA protease FtsH associates with HflK/C subunits to form a megadalton-size complex that spans the inner membrane and extends into the periplasm of E. coli. How this bacterial complex and homologous assemblies in eukaryotic organelles recruit, extract, and degrade membrane-embedded substrates is unclear. Following the overproduction of protein components, recent cryo-EM structures showed symmetric HflK/C cages surrounding FtsH in a manner proposed to inhibit the degradation of membrane-embedded substrates. Here, we present structures of native protein complexes, in which HflK/C instead forms an asymmetric nautilus-shaped assembly with an entryway for membrane-embedded substrates to reach and be engaged by FtsH. Consistent with this nautilus-like structure, proteomic assays suggest that HflK/C enhances FtsH degradation of certain membrane-embedded substrates. Membrane curvature in our FtsH•HflK/C complexes is opposite that of surrounding membrane regions, a property that correlates with lipid scramblase activity and possibly with FtsH's function in the degradation of membrane-embedded proteins.
Keywords: AAA Protease; Cryo-EM; Macromolecular Complexes; Proteostasis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and competing interests statement. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Update of
-
An asymmetric nautilus-like HflK/C assembly controls FtsH proteolysis of membrane proteins.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 10:2024.08.09.604662. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.09.604662. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: EMBO J. 2025 May;44(9):2501-2513. doi: 10.1038/s44318-025-00408-1. PMID: 39149393 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Arends J, Thomanek N, Kuhlmann K, Marcus K, Narberhaus F (2016) In vivo trapping of FtsH substrates by label-free quantitative proteomics. Proteomics 16:3161–3172 - PubMed
-
- Bittner LM, Arends J, Narberhaus F (2017) When, how and why? Regulated proteolysis by the essential FtsH protease in Escherichia coli. Biol Chem 398:625–635 - PubMed
-
- Browman DT, Hoegg MB, Robbins SM (2007) The SPFH domain-containing proteins: more than lipid raft markers. Trends Cell Biol 17:394–402 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

