Transcriptomic and proteomic analyses of sclera in lens-induced myopic guinea pigs
- PMID: 40082769
- PMCID: PMC11905693
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-025-11422-2
Transcriptomic and proteomic analyses of sclera in lens-induced myopic guinea pigs
Abstract
Background: Myopia development is commonly assessed by an increase in axial length, which may lead to high myopia and visual impairment. This study aims to identify potential biomarkers and signaling pathways in the sclera during experimental axial elongation.
Methods: A myopia guinea pig model was established using male guinea pigs aged 2-3 weeks, which underwent bilateral lens-induced myopization (LIM) (study group) or were left untreated (control group). An integrated analysis of transcriptomic and proteomic was performed to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the sclera. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analyses were conducted to explore the DEGs related signaling pathways. Promising candidate markers were further tested by Western blot analysis. Transmission electron microscopy was used to assess scleral fiber changes in myopic guinea pigs.
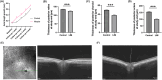
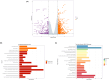
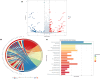
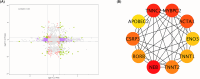
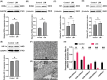
Results: During the study period, axial elongation was significantly greater in the study group (0.59 ± 0.05 mm vs. 0.47 ± 0.02 mm; P < 0.001), accompanied by a reduction in the thickness of the retina (121.9 ± 2.50 μm vs. 134.6 ± 0.48 μm; P < 0.001), choroid (38 ± 1.0 μm vs. 50 ± 0.8 μm; P < 0.001), and sclera (100.8 ± 2.78 μm vs. 155.6 ± 4.78 μm; P < 0.001). Integrated transcriptomic and proteomic analyses identified 34 upregulated genes, with significant activation and enrichment of the circadian rhythm pathway. Among the top enriched pathways, key differentially expressed genes included retinoid-related orphan receptors RORα and RORβ, which are recognized as critical signals modulating the scleral hypoxia response. Western blot analysis confirmed upregulation of RORα, RORβ, melatonin receptor type 1 (MT1), and HIF-1α in the sclera, while melatonin receptor type 2 (MT2) expression remained unchanged between the groups. Transmission electron microscopy revealed a significantly higher proportion of thin collagen fibers compared to thick fibers in the LIM group (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: Axial elongation-related remodeling of scleral collagen is closely linked to circadian rhythm and hypoxia pathways, with RORα, RORβ, melatonin receptors, and HIF-1α identified as potential key regulators. Additionally, scleral fiber size decreases progressively with scleral remodeling in myopia development.
Keywords: Lens-Induced myopia; Melatonin receptors; Proteomics; Retinoid-related orphan receptors (RORs); Transcriptomics.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participants: The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Beijing Tongren Hospital, ensuring compliance with the ARVO (Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology) statement for the use of animals in ophthalmic and vision research. All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations. It is confirmed that the study is reported in accordance with ARRIVE (Animal Research: Reporting of In Vivo Experiments) guidelines. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RNA sequencing analysis of long non-coding RNA expression in ocular posterior poles of guinea pig myopia models.Mol Vis. 2020 Mar 5;26:117-134. eCollection 2020. Mol Vis. 2020. PMID: 32180678 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of riboflavin/ultraviolet-A scleral collagen cross-linking on regional scleral thickness and expression of MMP-2 and MT1-MMP in myopic guinea pigs.PLoS One. 2023 Jan 18;18(1):e0279111. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0279111. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36652495 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Characteristics of Sclera in Lens-Induced Myopic Guinea Pigs.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024 Nov 4;65(13):51. doi: 10.1167/iovs.65.13.51. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024. PMID: 39585677 Free PMC article.
-
Candidate pathways for retina to scleral signaling in refractive eye growth.Exp Eye Res. 2022 Jun;219:109071. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2022.109071. Epub 2022 Apr 18. Exp Eye Res. 2022. PMID: 35447101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Scleral Changes in the Progression of Myopia: A Review and Future Directions.Clin Ophthalmol. 2025 May 23;19:1699-1707. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S523283. eCollection 2025. Clin Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40433505 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The correlation between intraocular pressure and choroidal microcirculation in patients with high myopia.Int J Med Sci. 2025 Jun 20;22(12):3032-3043. doi: 10.7150/ijms.113035. eCollection 2025. Int J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40657382 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li HY, Dong L, Shi XH, Zhang RH, Zhou W, Da, Wu HT, et al. Intraocular cetuximab: safety and effect on axial elongation in young guinea pigs with lens-induced myopization. Exp Eye Res. 2024;238:109715. - PubMed
-
- Morgan IG, Ohno-Matsui K, Saw SM. Myopia. Lancet. 2012;379:1739–48. - PubMed
-
- Gentle A, Liu Y, Martin JE, Conti GL, Mcbrien NA. Collagen gene expression and the altered accumulation of scleral collagen during the development of high myopia. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:16587–94. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

