Exercise-Induced Cardiac Lymphatic Remodeling Mitigates Inflammation in the Aging Heart
- PMID: 40083143
- PMCID: PMC12151892
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.70043
Exercise-Induced Cardiac Lymphatic Remodeling Mitigates Inflammation in the Aging Heart
Abstract
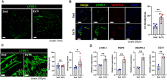
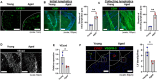
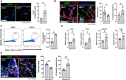
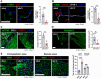
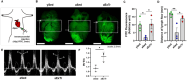
The lymphatic vasculature plays essential roles in fluid balance, immunity, and lipid transport. Chronic, low-grade inflammation in peripheral tissues develops when lymphatic structure or function is impaired, as observed during aging. While aging has been associated with a broad range of heart pathophysiology, its effect on cardiac lymphatic vasculature has not been characterized. Here, we analyzed cardiac lymphatics in aged 20-month-old mice versus young 2-month-old mice. Aged hearts showed reduced lymphatic vascular density, more dilated vessels, and increased inflammation and fibrosis in peri-lymphatic zones. As exercise has shown benefits in several different models of age-related heart disease, we further investigated the effects of aerobic training on cardiac lymphatics. Eight weeks of voluntary wheel running attenuated age-associated adverse remodeling of the cardiac lymphatics, including reversing their dilation, increasing lymph vessel density and branching, and reducing perilymphatic inflammation and fibrosis. Intravital lymphangiography demonstrated improved cardiac lymphatic flow after exercise training. Our findings illustrate that aging leads to cardiac lymphatic dysfunction, and that exercise can improve lymphatic health in aged animals.
Keywords: VEGF‐C; exercise; heart; lymphangiogenesis; lymphatic endothelial cells; lymphatic vessels; ventricular remodeling.
© 2025 The Author(s). Aging Cell published by Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
J.D.R. receives support from Amgen, Keros, and Genentech, along with the following patents (11,834,508, WO2018175460A1, US20180193529A1). J.R. consults for Takeda Neurosciences. All research support, patents, and consultancy are unrelated to this work.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R03HL177119/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL170048/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG061034/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21AG077040/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL155318/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL159514/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Wild Family Foundation
- 20CDA35310184/American Heart Association
- Rullo Family MGH Research Scholar
- R01 HL171201/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 23MERIT1038415/American Heart Association
- R21 AG077040/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG061034/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HT94252410100/U.S. Department of Defense
- R01 HL170058/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL140200/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 24SCEFIA1253853/American Heart Association
- R01 HL162928/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Fred and Ines Yeatts Fund for Innovative Research
- R03 HL177119/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL159514/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL171201/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01AG080077/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 22TPA969625/American Heart Association
- Foundation for Anesthesia Education and Research MRTG
- K08HL140200/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- SFRN 026415-00001/American Heart Association
- K01 AG080077/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL162928/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL142809/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RS-2024-00359396/National Research Foundation of Korea
- R01HL142809/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35HL155318/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Hassenfeld Scholars Award
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

