Brain Morphometrics Correlations With Age Among 350 Participants Imaged With Both 3T and 7T MRI: 7T Improves Statistical Power and Reduces Required Sample Size
- PMID: 40083197
- PMCID: PMC11907059
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.70195
Brain Morphometrics Correlations With Age Among 350 Participants Imaged With Both 3T and 7T MRI: 7T Improves Statistical Power and Reduces Required Sample Size
Abstract
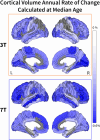
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at 7T has a superior signal-to-noise ratio to 3T but also presents higher signal inhomogeneities and geometric distortions. A key knowledge gap is to robustly investigate the sensitivity and accuracy of 3T and 7T MRI in assessing brain morphometrics. This study aims to (a) aggregate a large number of paired 3T and 7T scans to evaluate their differences in quantitative brain morphological assessment using a widely available brain segmentation tool, FreeSurfer, as well as to (b) examine the impact of normalization methods for subject variability and smaller sample sizes on data analysis. A total of 401 healthy participants aged 29-68 were imaged at both 3T and 7T. Structural T1-weighted magnetization-prepared rapid gradient-echo (MPRAGE) images were processed and segmented using FreeSurfer. To account for head size variability, the brain volumes underwent intracranial volume (ICV) correction using the Residual (regression model) and Proportional (simple division to ICV) methods. The resulting volumes and thicknesses were correlated with age using Pearson's correlation and false discovery rate correction. The correlations were also calculated in increasing sample size from three to the whole sample to estimate the sample size required to detect aging-related brain variation. Three hundred and fifty subjects (208 females) passed the image quality control, with 51 subjects excluded due to excessive motion artifacts on 3T, 7T, or both. 7T MRI showed an overall stronger correlation between morphometrics and age and a larger number of significantly correlated brain volumes and cortical thicknesses. While the ICV is consistent between both field strengths, the Residual normalization method shows markedly higher correlation with age for 3T when compared with the Proportional normalization method. The 7T results are consistent regardless of the normalization method used. In a large cohort of healthy participants with paired 3T and 7T scans, we compared the statistical performance in assessing age-related brain morphological changes. Our study reaffirmed the inverse correlation between brain volumes and cortical thicknesses and age and highlighted varying correlations in different brain regions and normalization methods at 3T and 7T. 7T imaging significantly improves statistical power and thus reduces the required sample size.
Keywords: 3T; 7T; aging; brain morphometrics; magnetic resonance imaging.
© 2025 The Author(s). Human Brain Mapping published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
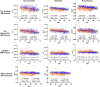
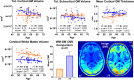
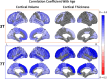
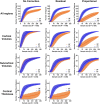

Update of
-
Brain morphometrics correlations with age among 352 participants imaged with both 3T and 7T MRI: 7T improves statistical power and reduces required sample size.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 1:2024.10.28.24316292. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.28.24316292. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Hum Brain Mapp. 2025 Mar;46(4):e70195. doi: 10.1002/hbm.70195. PMID: 39574870 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Brain morphometrics correlations with age among 352 participants imaged with both 3T and 7T MRI: 7T improves statistical power and reduces required sample size.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 1:2024.10.28.24316292. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.28.24316292. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Hum Brain Mapp. 2025 Mar;46(4):e70195. doi: 10.1002/hbm.70195. PMID: 39574870 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Magnetic resonance perfusion for differentiating low-grade from high-grade gliomas at first presentation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 22;1(1):CD011551. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011551.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29357120 Free PMC article.
-
MarkVCID cerebral small vessel consortium: II. Neuroimaging protocols.Alzheimers Dement. 2021 Apr;17(4):716-725. doi: 10.1002/alz.12216. Epub 2021 Jan 21. Alzheimers Dement. 2021. PMID: 33480157 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Rathke Cleft and Other Incidental Pituitary Gland Findings on Contrast-Enhanced 3D Fat-Saturated T1 MPRAGE at 7T MRI.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2024 Nov 7;45(11):1811-1818. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A8393. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2024. PMID: 38914432
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
RF shimming strategy for an open 60-channel RF transmit 7T MRI head coil for routine use on the single transmit mode.Magn Reson Med. 2025 Oct;94(4):1804-1816. doi: 10.1002/mrm.30563. Epub 2025 May 20. Magn Reson Med. 2025. PMID: 40391665 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-Modality Image Translation of 3 Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging to 7 Tesla Using Generative Adversarial Networks.Hum Brain Mapp. 2025 Jun 15;46(9):e70246. doi: 10.1002/hbm.70246. Hum Brain Mapp. 2025. PMID: 40545512 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrea, N. , Sajewski T. S., De Franco A., et al. 2024. “RF Shimming Strategy for an Open 60‐Channel RF Transmit 7T Head Coil for Routine Use on the Single Transmit Mode.” medRxiv.
-
- Andrea, N. , Sajewski T. S., De Franco A., et al. 2023. “An Open 60‐Channel Tx/ 32‐Channel Rx RF Coil System for Routine Use at 7T ISMRM.”
-
- Benjamini, Y. , and Hochberg Y.. 1995. “Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing.” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B: Methodological 57, no. 1: 289–300. http://www.jstor.org.pitt.idm.oclc.org/stable/2346101.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

