TMEM105 modulates disulfidptosis and tumor growth in pancreatic cancer via the β-catenin-c-MYC-GLUT1 axis
- PMID: 40083702
- PMCID: PMC11900826
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.104598
TMEM105 modulates disulfidptosis and tumor growth in pancreatic cancer via the β-catenin-c-MYC-GLUT1 axis
Abstract
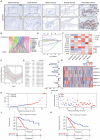
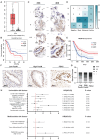
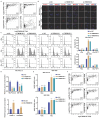
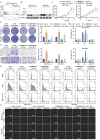
Background: Pancreatic cancer (PCa) is one of the most malignant diseases in the world. Different from ferroptosis and apoptosis, disulfidptosis is a novel type of cell death. The role of disulfidptosis in PCa remains uncovered. Methods: Disulfidptosis-related lncRNAs were identified based on TCGA-PAAD database. The disulfidptosis-related predict signature was constructed and verified by bioinformatic analysis. TCGA and GTEx database and Renji tissue microarray (TMA) were applied to determine TMEM105 and its clinical significance. F-actin and PI staining were performed to detect disulfidptosis of PCa cells. The biological function of TMEM105 was investigated by loss-of-function and gain-of-function assays. RNA pull-down and LC-MS/MS analysis were employed to detect TMEM105 interacted proteins. The tissue samples from PCa patients with PET-CT information were utilized to validate the TMEM105-β-catenin-c-MYC-GLUT1 pathway in clinical settings. Results: A disulfidptosis-related predict signature, which was comprised of six lncRNAs, was constructed and validated by bioinformatic analysis. TMEM105 was identified as disulfidptosis-related lncRNA whose high expression predicted a poor prognosis in PCa. Functional studies revealed that TMEM105 promoted the growth and mitigated the disulfidptosis in PCa. Mechanically, TMEM105 upregulated the expression of β-catenin by maintaining the protein stability through the proteosome pathway. The forced expressed β-catenin increased the expression of glycolysis-related transcription factor c-MYC, thus induced the transcription activity of GLUT1. Conclusion: These results revealed the growth acceleration and the disulfidptosis mitigation function of TMEM105 in PCa. Targeting the TMEM105-β-catenin-c-MYC-GLUT1 pathway could be a potent therapy for PCa patients.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


References
-
- Guo X, Cui Z. Current diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic cancer in China. Pancreas. 2005;31:13–22. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:7–33. - PubMed
-
- Traub B, Link KH, Kornmann M. Curing pancreatic cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 2021;76:232–46. - PubMed
-
- Zhang S, Yao HF, Li H, Su T, Jiang SH, Wang H. et al. Transglutaminases are oncogenic biomarkers in human cancers and therapeutic targeting of TGM2 blocks chemoresistance and macrophage infiltration in pancreatic cancer. Cell Oncol (Dordr) 2023;46:1473–92. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

