OLFML3 Promotes IRG1 Mitochondrial Localization and Modulates Mitochondrial Function in Macrophages
- PMID: 40083707
- PMCID: PMC11900800
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.103859
OLFML3 Promotes IRG1 Mitochondrial Localization and Modulates Mitochondrial Function in Macrophages
Abstract
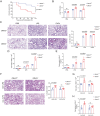
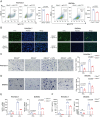
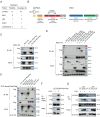
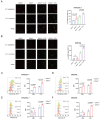
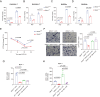
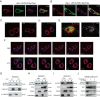
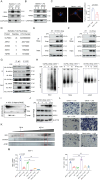
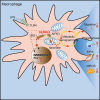
Olfactomedin-like protein 3 (OLFML3), belonging to olfactomedin (OLF) protein family, has poorly defined functions. Recent studies have reported the functions of OLFML3 in anti-viral immunity and tumorigenesis. In this study, we investigated the roles of OLFML3 in macrophages. In LPS- or Pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced acute lung injury (ALI) mouse model, OLFML3 depletion exacerbated inflammatory response, leading to reduced survival. OLFML3 achieved the in vivo activity by regulating macrophage phagocytosis and migration. Mass spectrometry analysis revealed immunoresponsive gene 1 (IRG1) as an OLFML3-interacting protein. IRG1 is a mitochondrial decarboxylase that catalyzes the conversion of cis-aconitate to itaconate, a myeloid-borne mitochondrial metabolite with immunomodulatory activities. Further investigation showed that OLFML3 could prevent LPS-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in macrophages by maintaining the homeostasis of mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (mtROS) and itaconate-related metabolites. In-depth protein-protein interaction studies showed that OLFML3 could promote IRG1 mitochondrial localization via a mitochondrial transport protein, apoptosis inducing factor mitochondria associated 1 (AIFM1). In summary, our study showed that OLFML3 could facilitate IRG1 mitochondrial localization and prevent LPS-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in macrophages.
Keywords: IRG1; OLFML3; acute Lung Injury; macrophage; mitochondria.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Zeng LC, Liu F, Zhang X, Zhu ZD, Wang ZQ, Han ZG. et al. hOLF44, a secreted glycoprotein with distinct expression pattern, belongs to an uncharacterized olfactomedin-like subfamily newly identified by phylogenetic analysis. FEBS Lett. 2004;571:74–80. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed F, Torrado M, Zinovieva RD, Senatorov VV, Wistow G, Tomarev SI. Gene expression profile of the rat eye iridocorneal angle: NEIBank expressed sequence tag analysis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004;45:3081–90. - PubMed
-
- Ikeya M, Kawada M, Nakazawa Y, Sakuragi M, Sasai N, Ueno M. et al. Gene disruption/knock-in analysis of mONT3: vector construction by employing both in vivo and in vitro recombinations. Int J Dev Biol. 2005;49:807–23. - PubMed
-
- Sakuragi M, Sasai N, Ikeya M, Kawada M, Onai T, Katahira T. et al. Functional analysis of chick ONT1 reveals distinguishable activities among olfactomedin-related signaling factors. Mech Dev. 2006;123:114–23. - PubMed
-
- Inomata H, Haraguchi T, Sasai Y. Robust stability of the embryonic axial pattern requires a secreted scaffold for chordin degradation. Cell. 2008;134:854–65. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

