Radiofrequency electromagnetic field ınhibits HIF-1 alpha and activates eNOS signaling to prevent intestinal damage in a model of mesenteric artery ischemia in rats
- PMID: 40084245
- PMCID: PMC11898852
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.105479
Radiofrequency electromagnetic field ınhibits HIF-1 alpha and activates eNOS signaling to prevent intestinal damage in a model of mesenteric artery ischemia in rats
Abstract
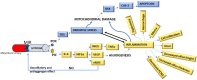
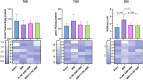
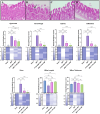
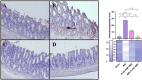
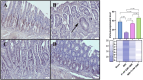
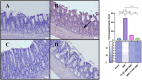
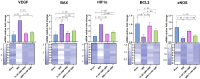
Background: Pathologies such as mesenteric artery ischemia and reperfusion (MIR) can lead to many organ dysfunctions, including the brain and heart through damage mechanisms induced in response to hypoxic conditions. Radiofrequency electromagnetic field (RF-EMF) can increase the vascularization of tissues by providing endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS)-mediated nitric oxide (NO) release from the endothelium. The aim of this study is to investigate the protective effect and mechanism of RF-EMF in ischemic intestinal injury in the experimental MIR model. Methods: In the study, 32 Wistar Albino rats were divided into four groups: Sham group, MIR group, Prophylactic (Pr) RF-EMF + MIR group, MIR + Therapeutic (Tr) RF-EMF group. At the end of the experimental phase, after sacrifice, blood samples and the 10 cm terminal ileum part of the intestinal tissues was cut and collected for histopathological, immunohistochemical, genetic and biochemical analyses. Results: In the MIR group, Cas-3, TNF-α, VEGF, BAX and HIF-1α expressions increased, while OSI levels, and PCNA, BCL2 and eNOS expressions decreased. In addition marked hyperemia, hemorrhage, edema, inflammatory cell infiltrations, and erosion or ulcers were observed in MIR group. Pr (especially in eNOS expression) and Tr (especially in pathological findings) treatment of RF-EMF reversed all these parameters but more effective recovery was observed in Tr treated group. Conclusion: RF-EMF-treatment preserved the vascularization of the tissue and decreased hypoxia-induced oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Electromagnetic field; Mesenteric ischemia; Oxidative stress Radiofrequency.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

