INCEPT: The Intensive Care Platform Trial-Design and protocol
- PMID: 40084471
- PMCID: PMC11907384
- DOI: 10.1111/aas.70023
INCEPT: The Intensive Care Platform Trial-Design and protocol
Abstract
Background: Adult intensive care unit (ICU) patients receive many interventions, but few are supported by high-certainty evidence. Randomised clinical trials (RCTs) are essential for trustworthy comparisons of intervention effects, but conventional RCTs are costly, cumbersome, inflexible, and often turn out inconclusive. Adaptive platform trials may mitigate these issues and have higher probabilities of obtaining conclusive results faster and at lower costs per participant.
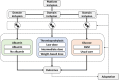
Methods: The Intensive Care Platform Trial (INCEPT) is an investigator-initiated, pragmatic, randomised, embedded, multifactorial, international, adaptive platform trial including adults acutely admitted to ICUs. INCEPT will assess comparable groups of interventions (primarily commonly used interventions with clinical uncertainty and practice variation) nested in domains. Interventions may be either open-label or masked. New domains will continuously be added to the platform. INCEPT assesses multiple core outcomes selected following substantial stakeholder involvement: mortality, days alive without life support/out of hospital/free of delirium, health-related quality of life, cognitive function, and safety outcomes. Each domain will use one of these core outcomes as the primary outcome. INCEPT primarily uses Bayesian statistical methods with neutral, minimally informative or sceptical priors, adjustment for important prognostic baseline variables, and calculation of absolute and relative differences in the intention-to-treat populations. Domains and intervention arms may be stopped for superiority/inferiority, practical equivalence, or futility according to pre-specified adaptation rules evaluated using statistical simulation or at pre-specified maximum sample sizes. Domains may use response-adaptive randomisation, meaning that more participants will be allocated to interventions with higher probabilities of being superior.
Conclusions: INCEPT provides an efficient, pragmatic, and flexible platform for comparing the effects of many interventions used in adult ICU patients. The adaptive design enables the trial to use accumulating data to improve the treatment of future participants. INCEPT will provide high-certainty, conclusive evidence for many interventions, directly inform clinical practice, and thus improve patient-important outcomes.
Keywords: adaptive platform trial; intensive care; randomised clinical trial; trial protocol.
© 2025 The Author(s). Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica Foundation.
Conflict of interest statement
Bodil Steen Rasmussen: unrestricted grant from the Novo Nordisk Foundation for long‐term follow‐up in the Handling Oxygenation Targets in the Intensive Care Unit (HOT‐ICU) trial (ended June 2024). Tine Sylvest Meyhoff: coordinating investigator of the CLASSIC trial (NCT03668236) which was supported by a grant (NNF17OC0028608) from the Novo Nordisk Foundation and by the Sofus Friis' Foundation, Rigshospitalet's Research Council, and supported by the Danish Society of Anesthesiology and Intensive Care Medicine. Hans‐Christian Thorsen‐Meyer: research grant from the Novo Nordisk Foundation (NNF19OC0054863). Marie Oxenbøll Collet: the Novo Nordisk Foundation, Grant NNF21OC0072048 Postdoc fellowships in Nursing Research 2021. Ole Mathiesen: funding to research group from the Novo Nordisk Foundation and Sygeforsikringen ‘danmark’ for other projects. Mathias Maagaard: holds shares in Novo Nordisk. Peter Rossing: grants for investigator‐initiated studies to Steno Diabetes Center Copenhagen, from Novo Nordisk, Bayer, AstraZeneca, and Lexicon. Honoraria to Steno Diabetes Center Copenhagen for steering group membership, consultancy, and education from AstraZeneca, Abbott, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Gilead, and Sanofi. No personal honoraria and no shares/patents. Asger Granfeldt: paid member of data safety monitoring board for Noorik Pharmaceuticals (ended November 2022), work for hire for NMD Pharma, and task force member of the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR) advanced life support task force. Theis Skovsgaard Itenov: the Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care, Copenhagen University Hospital—Bispebjerg and Frederiksberg Hospital has a collaboration with Radiometer Medical Denmark on the testing and evaluation of equipment. The department receives reimbursements from the company. No individual receives any personal benefits or payments from the collaboration. Johanna Hästbacka: advisory board honorary fee from Paion (2022). Carmen Andrea Pfortmueller: no personal conflict of interests (personal financial interest). The department of Intensive Care at Inselspital, University Hospital of Bern reports grants from Orion Pharma, Abbott Nutrition International, B. Braun Medical AG, CSEM AG, Edwards Lifesciences Services GmbH, Kenta Biotech Ltd., Maquet Critical Care AB, Omnicare Clinical Research AG, Nestle, Pierre Fabre Pharma AG, Pfizer, Bard Medica S.A., Abbott AG, Anandic Medical Systems, Pan Gas AG Healthcare, Bracco, Hamilton Medical AG, Fresenius Kabi, Getinge Group Maquet AG, Dräger AG, Teleflex Medical GmbH, Glaxo Smith Kline, Merck Sharp and Dohme AG, Eli Lilly and Company, Baxter, Astellas, Astra Zeneca, CSL Behring, Novartis, Covidien, and Nycomed outside the submitted work. The money was paid into departmental funds; no personal financial gain applied. Davide Placido: holds stocks in Novo Nordisk. Theis Lange: served on data safety monitoring boards in studies run by Novo Nordisk and Leo Pharma. Anders Perner: research grants from the Novo Nordisk Foundation. All other authors: no relevant conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dansk Intensiv Database . Årsrapport 2024. 2024. www.sundk.dk Accessed February 27, 2025.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

