Failure to Close: An Unexpected Surgical Complication Reveals OTULIN Haploinsufficiency
- PMID: 40084498
- PMCID: PMC11907234
- DOI: 10.1002/acr2.11800
Failure to Close: An Unexpected Surgical Complication Reveals OTULIN Haploinsufficiency
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this report is to raise awareness of a rare inborn error of immunity (IEI) that can predispose to inflammatory disease and infection risk by describing a patient case.
Methods: We reviewed clinical findings, laboratory and pathology evaluations, and genetic results.
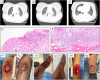
Results: A 13-year-old female patient with a history of prematurity and spastic diplegic cerebral palsy underwent planned orthopedic procedures to correct chronic gait abnormalities. Her postoperative course was complicated by fevers associated with respiratory failure and wound dehiscence at the surgical sites. A chest computed tomography scan revealed bilateral consolidative pneumonia with parapneumonic effusions. Infectious and clinical immune evaluations were unremarkable. She had resolution of fevers and respiratory failure with broad-spectrum antibiotics; however, her wounds became progressively ulcerative and necrotic. A skin biopsy demonstrated skin ulceration with acute neutrophilic inflammation. She was started on glucocorticoids and infliximab infusions with prompt improvement in wound healing. Subsequently, a clinical genetic panel revealed a heterozygous variant in OTULIN c.787C>T, p.Arg263Trp, located at the same amino acid previously reported in OTULIN haploinsufficiency. OTULIN haploinsufficiency is a rare IEI that predisposes to life-threatening necrosis of the skin and lungs, often in response to Staphylococcus aureus infection.
Conclusion: OTULIN haploinsufficiency predisposes to increased susceptibility to infections and tissue-specific necrosis often triggered by infection. Recognition of this rare IEI is important because patients with OTULIN haploinsufficiency may require combined antibiotic and immunomodulatory therapy.
© 2025 The Author(s). ACR Open Rheumatology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American College of Rheumatology.
Figures
References
-
- Iwai K, Fujita H, Sasaki Y. Linear ubiquitin chains: NF‐κB signalling, cell death and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2014;15(8):503–508. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

