Inhibiting EZH2 complements steroid effects in Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- PMID: 40085707
- PMCID: PMC11908487
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adr4443
Inhibiting EZH2 complements steroid effects in Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Abstract
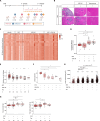
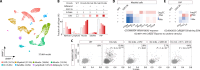
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a devastating X-linked disorder caused by dystrophin gene mutations. Despite recent advances in understanding the disease etiology and applying emerging treatment methodologies, glucocorticoid derivatives remain the only general therapeutic option that can slow disease development. However, the precise molecular mechanism of glucocorticoid action remains unclear, and there is still need for additional remedies to complement the treatment. Here, using single-nucleus RNA sequencing and spatial transcriptome analyses of human and mouse muscles, we investigated pathogenic features in patients with DMD and palliative effects of glucocorticoids. Our approach further illuminated the importance of proliferating satellite cells and revealed increased activity of a signal transduction pathway involving EZH2 in the patient cells. Subsequent administration of EZH2 inhibitors to Dmd mutant mice resulted in improved muscle phenotype through maintaining the immune-suppressing effect but overriding the muscle weakness and fibrogenic effects exerted by glucocorticoids. Our analysis reveals pathogenic mechanisms that can be readily targeted by extant therapeutic options for DMD.
Figures




References
-
- Mah J. K., Korngut L., Dykeman J., Day L., Pringsheim T., Jette N., A systematic review and meta-analysis on the epidemiology of Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy. Neuromuscul. Disord. 24, 482–491 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Hoy S. M., Delandistrogene moxeparvovec: First approval. Drugs 83, 1323–1329 (2023). - PubMed
-
- FDA, FDA Approves First Gene Therapy for Treatment of Certain Patients with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (FDA, 2023); https://fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-gene-....
-
- Lek A., Wong B., Keeler A., Blackwood M., Ma K., Huang S., Sylvia K., Batista A. R., Artinian R., Kokoski D., Parajuli S., Putra J., Carreon C. K., Lidov H., Woodman K., Pajusalu S., Spinazzola J. M., Gallagher T., LaRovere J., Balderson D., Black L., Sutton K., Horgan R., Lek M., Flotte T., Death after high-dose rAAV9 gene therapy in a patient with Duchenne's muscular dystrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 389, 1203–1210 (2023). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

