Early daratumumab therapy improves renal outcomes in newly diagnosed patients with myeloma admitted with kidney injury
- PMID: 40085948
- PMCID: PMC12242421
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2025015901
Early daratumumab therapy improves renal outcomes in newly diagnosed patients with myeloma admitted with kidney injury
Abstract
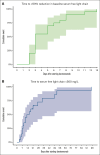
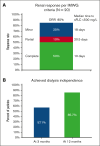
Cast nephropathy is the most common cause of acute kidney injury (AKI) in patients with multiple myeloma (MM). A prompt reversal of renal injury is paramount for improving clinical outcomes. Daratumumab, an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody, has significant clinical efficacy in MM. We describe the effects of daratumumab-based therapy in 20 patients admitted with a new diagnosis of MM and AKI with a median creatinine of 6.5 mg/dL. All patients (100%) achieved serum free light chain (sFLC) reduction ≥50% within the first cycle, with a median time to sFLC reduction ≥50% of 3 days (95% confidence interval [CI], 3-7). Of 17 patients, 15 (88%) achieved sFLC reduction ≤500 mg/L after 1 cycle of treatment. The median time to sFLC reduction ≤500 mg/L was 14.5 days (95% CI, 9-49). The overall renal response at 3 months was 85% (n = 17), with complete, partial, and minor responses in 50% (n = 10), 10% (n = 2), and 25% (n = 5), respectively. Of the 9 patients who required dialysis at presentation, 4 of 7 (57.1%) and 6 of 7 (85.7%) were dialysis independent at 3 and 12 months, respectively. Hematologic overall response rate was 100%, with very good partial response (VGPR) in 90%. With a median follow-up of 25 months, progression-free survival was 46.5 months (95% CI, 11.9 to not reached), and the 2-year overall survival was 83.7% (95% CI, 68.4-100). These findings highlight the importance of early initiation of daratumumab-based treatment in patients with MM and AKI to induce rapid and significant reductions in sFLCs, improve renal outcomes, and provide an approach without plasmapheresis.
© 2025 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: M.L. reports consulting for BTG Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Genentech, Genmab, and MJH Life Sciences. E.K.O. reports consulting for Janssen, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), Sanofi, Pfizer, Exact Sciences, and Grail; and steering committee fees from Natera. D.C. reports consulting for Sanofi. N.S.R. reports consulting for AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, Janssen, Pfizer, Immuneel, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), K36 Therapeutics, Sanofi, and AstraZeneca; and research funding from Pfizer. A.J.Y. reports consulting for AbbVie, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Amgen, BMS, Celgene, GSK, Johnson & Johnson (Janssen), Karyopharm, Oncopeptides, Pfizer, Prothena, Regeneron, Sanofi, Sebia, and Takeda; and research funding to institution from Amgen, BMS, GSK, Johnson & Johnson (Janssen), and Sanofi. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
The current affiliation for E.K.O. is Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, MA.
Figures

References
-
- Dimopoulos MA, Merlini G, Bridoux F, et al. Management of multiple myeloma-related renal impairment: recommendations from the International Myeloma Working Group. Lancet Oncol. 2023;24(7):e293–e311. - PubMed
-
- Eleutherakis-Papaiakovou V, Bamias A, Gika D, et al. Renal failure in multiple myeloma: incidence, correlations, and prognostic significance. Leuk Lymphoma. 2007;48(2):337–341. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

