Structural brain alterations and changes in resting-state functional connectivity in patients with trigeminal neuralgia: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 40086208
- PMCID: PMC11954123
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nicl.2025.103759
Structural brain alterations and changes in resting-state functional connectivity in patients with trigeminal neuralgia: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is a chronic pain condition characterized by severe, electric shock-like pain in one or more branches of the trigeminal nerve. Even though neuroimaging studies have highlighted alterations in brain cortical and subcortical structure and functional connectivity, findings are heterogeneous.
Objective: This meta-analysis aims to synthesize structural and functional brain changes in TN patients through a coordinate-based meta-analysis using GingerALE.
Methods: A search on PubMed, Google Scholar, and Scopus was conducted to select pertinent publications on structural magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (brain volume and cortical thickness) and resting-state functional MRI in TN patients that were published before January 2024. Activation likelihood estimation (ALE) was used to identify consistent brain alteration patterns across studies.
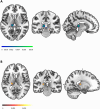
Results: A total of 1436 papers were identified and, after review based on the predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria, 13 papers (538 patients) discussing structural brain changes and 11 studies (368 patients) discussing resting-state functional connectivity studies were selected for inclusion. Structural and functional alterations in TN were observed in the left thalamus.
Conclusions: This meta-analysis provides a comprehensive examination of structural and functional abnormalities in TN patients, highlighting consistent alterations in left thalamus. Future research should identify brain structural and functional changes specific for TN as compared to other forms of chronic pain, explore longitudinal changes correlated to clinical parameters, and perform intra-population studies to address lateralization, to enhance diagnostic and therapeutic outcomes for TN patients.
Keywords: Chronic pain; Magnetic resonance imaging; Meta-analysis; Resting-state functional connectivity; Structural brain changes; Trigeminal Neuralgia.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Albano L., Agosta F., Basaia S., Castellano A., Messina R., Parisi V., Barzaghi L.R., Falini A., Mortini P., Filippi M. Alterations of brain structural MRI are associated with outcome of surgical treatment in trigeminal neuralgia. Euro J. Neurol. 2022;29:305–317. doi: 10.1111/ene.15105. - DOI - PubMed
-
- De Stefano G., Litewczuk D., Mollica C., Di Pietro G., Galosi E., Leone C., Falco P., Tullo M.G., Caramia F., Truini A., Di Stefano G. Sex differences in trigeminal neuralgia: a focus on radiological and clinical characteristics. Neurol. Sci. 2023;44:4465–4472. doi: 10.1007/s10072-023-06923-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

