Early Achievement of High Treatment Targets in Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis with Upadacitinib: Real-World Evidence from the Observational UP-TAINED Study
- PMID: 40087231
- PMCID: PMC11971103
- DOI: 10.1007/s13555-025-01373-7
Early Achievement of High Treatment Targets in Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis with Upadacitinib: Real-World Evidence from the Observational UP-TAINED Study
Abstract
Introduction: Phase 3 clinical trials have demonstrated robust efficacy and favorable safety of upadacitinib for the treatment of atopic dermatitis (AD). However, real-world data are still sparse. The objectives of this study were to assess the effectiveness and safety of real-world treatment with upadacitinib in patients with moderate-to-severe AD.
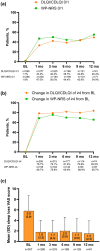
Methods: UP-TAINED is an ongoing German prospective, multicenter, observational study in adolescents and adults with moderate-to-severe AD treated with upadacitinib 15 or 30 mg once daily, according to local labeling. Effectiveness (primary endpoint; measured with the Atopic Dermatitis Control Tool [ADCT]) and safety are assessed over 2 years. Reported here are 1-year results from an interim analysis.
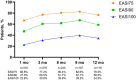
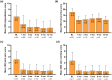
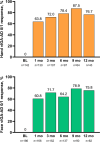
Results: Data on 351 patients were included in the effectiveness analysis. At 12 weeks, 71.0% of patients had achieved disease control (ADCT total score < 7); at 1 year, this rate was 70.9%. An Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) ≤ 3 was achieved by 60.6% of patients after 4 weeks and 68.1% after 1 year of upadacitinib treatment. Of 186 patients with moderate-to-severe facial eczema at baseline and 142 patients with moderate-to-severe hand eczema at baseline, 60.8% (101/166) and 63.8% (83/101) achieved clear or almost clear skin in those respective body regions after 4 weeks of upadacitinib treatment. Of the 380 patients included in the safety analysis, 163 patients reported 426 adverse events (AEs), most classified as mild (59.7%) or moderate (34.6%). The most common AEs were (worsening of) AD, acne, and COVID-19. No major cardiovascular AEs, venous thromboembolism, or malignancies were reported.
Conclusions: Upadacitinib was well tolerated, and the majority of patients with moderate-to- severe AD receiving upadacitinib in real-world clinical practice achieved stringent treatment goals with early and up to 1-year disease control attained, particularly in difficult-to-treat areas such as hand and face.
Clinical trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT05139836.
Keywords: Atopic dermatitis; Disease control; Eczema; Germany; Real-world treatment; Upadacitinib.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of Interest: Stephan Weidinger received institutional research grants from LEO Pharma, Pfizer, and Sanofi Deutschland GmbH and lecture and/or consultancy fees from AbbVie, Almirall, Boehringer, Eli Lilly, Galderma, GSK, LEO Pharma, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi. He is involved in performing clinical trials with many pharmaceutical industries that manufacture drugs used for the treatment of psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. Tobias Schadeck participated in noninterventional trials for AbbVie. Felix Jacobs is a member of advisory boards and/or a speaker for AbbVie, Alliance Pharma, Almirall, Hermal, Janssen, Lilly, and Novartis. Ansgar Weyergraf served as a speaker, advisor, and/or researcher for AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, Arctic Bioscience, Biogen, Bristol-Myers-Squibb, Celgene, Hermal, Janssen, LEO, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, and UCB. Dariusch Mortazawi was an advisor, received honoraria and grants, and/or participated in clinical trials for AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen-Cilag, LEO Pharma, Moberg Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Sandoz, Sanofi Genzyme, UCB Pharma, and Viatris. Tobias Hagemann is a member of advisory boards and/or a speaker for AbbVie, Almirall Hermal, Bencard Allergie GmbH, Pierre Fabre Dermatologie, Regeneron, and Sanofi-Aventis. Fatima Abousamra, Thomas Mosch, and Bjoern Fritz are employees of AbbVie and may own AbbVie stock. Felix Lauffer is a member of advisory boards and/or a speaker for AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, Biogen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers-Squibb, Janssen, LEO Pharma, Lilly, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi, UCB, and Union Therapeutics. Ethical Approval: According to the requirements for non-interventional, observational studies, no additional diagnostic or monitoring procedures or measurements that would not be feasible for use in routine clinical care were done in this study. Study-related monitoring, if applicable, was permitted by the study sites/investigators, including audits, independent ethics committee or independent review board review, and regulatory inspection(s). Ethics committee approval was obtained by the medical faculty in Kiel, Germany, on November 1, 2021.
Figures

References
-
- Langan SM, Irvine AD, Weidinger S. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet. 2020;396(10247):345–60. - PubMed
-
- Barbarot S, Auziere S, Gadkari A, et al. Epidemiology of atopic dermatitis in adults: results from an international survey. Allergy. 2018;73(6):1284–93. - PubMed
-
- Silverberg JI, Simpson B, Abuabara K, et al. Prevalence and burden of atopic dermatitis involving the head, neck, face, and hand: a cross sectional study from the TARGET-DERM AD cohort. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89(3):519–28. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

