Social disadvantage accelerates aging
- PMID: 40087516
- PMCID: PMC12092251
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-025-03563-4
Social disadvantage accelerates aging
Abstract
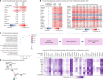
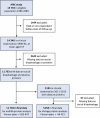
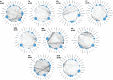
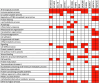
Social disadvantage, like advanced age, is a risk factor for a broad range of health conditions; however, whether it influences the aging process remains unclear. Here, using a multicohort approach, we investigated the associations of social disadvantage with age-related plasma proteins and age-related diseases. We found proteomic signatures of accelerated immune aging and 14 specific age-related proteins linked to social disadvantage during both early and later life. Individuals experiencing social disadvantage had an increased risk of 66 age-related diseases, with up to 39% of these associations mediated by the 14 age-related proteins (for example, DNAJB9, F2, HSPA1A, BGN). The main enriched pathway involved the upregulation of the pro-inflammatory regulator NF-κB24 and its downstream factor interleukin-8. Our findings support the hypothesis that social disadvantage throughout the life course may accelerate aging, a biological mechanism that could explain why social stratification plays such a fundamental role in determining human health.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: T.W-C. has filed a patent application related to proteomic organ aging, is a co-founder and scientific advisor of Teal Omics Inc. and has received equity stakes. T.W.-C. is also a co-founder and scientific advisor of Alkahest Inc. and Qinotto Inc. and has received equity stakes in these companies. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








References
-
- Kivimaki, M. et al. Association between socioeconomic status and the development of mental and physical health conditions in adulthood: a multi-cohort study. Lancet Public Health5, e140–e149 (2020). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- S011676, Y014154/Wellcome Trust (Wellcome)
- 75N92022D00002/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG056477/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)
- 75N92022D00003/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 339568/Academy of Finland (Suomen Akatemia)
- 75N92022D00001/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG056477/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92022D00004/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 221854/Z/20/Z/Wellcome Trust (Wellcome)
- 75N92022D00005/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 350426/Academy of Finland (Suomen Akatemia)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

