Dynamics of SERPINA3 in response to anthracycline treatment and cardiovascular dysfunction
- PMID: 40087712
- PMCID: PMC11907982
- DOI: 10.1186/s40959-025-00324-7
Dynamics of SERPINA3 in response to anthracycline treatment and cardiovascular dysfunction
Abstract
Background: SERPINA3 recently emerged as potential prognostic biomarker in heart failure. In a population of cancer survivors with cancer therapy-related cardiac dysfunction (CTRCD) circulating SERPINA3 was elevated compared to age-matched controls. We aimed to assess the longitudinal dynamics of circulating SERPINA3 levels in patients with cancer treated with anthracycline chemotherapy (AnC) and its relation to CTRCD.
Methods: In this single centre cohort study, 55 patients with cancer scheduled for AnC were prospectively enrolled. Cardiac evaluation (echocardiography, high-sensitive cardiac troponin I and NT-proBNP) was performed and SERPINA3 levels in plasma were assessed at 4 timepoints: before chemotherapy, directly after the end of chemotherapy, three months and twelve months after the end of chemotherapy.
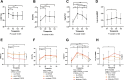
Results: Forty-two out of 55 patients (76.4%) developed CTRCD within 1 year after end of treatment. CTRCD was mild in 32 and moderate in 10 patients, defined as a change in cardiac biomarkers or GLS and LVEF decline < 50% respectively. Overall, median SERPINA3 levels decreased from baseline to three months after AnC (215.7 [62.0-984.0] to 176.9 [94.7-678.0] µg/ml, p = 0.031). This decrease was most prominent in patients without CTRCD (30.8% decrease, p = 0.007), followed by mild CTRCD (9.0% decrease, p = 0.022), while patients with moderate CTRCD did not show a reduction in SERPINA3 (5.1% increase, p = 0.987). SERPINA3 values at three months after AnC were positively correlated with NT-proBNP (r = 0.47, p = 0.002). Several malignancy, treatment and patient characteristics were associated with higher SERPINA3 values.
Conclusion: Circulating SERPINA3 levels show dynamic changes in a population of patients with cancer, with an overall decrease following AnC. However, in patients that developed moderate CTRCD, SERPINA3 levels remained elevated. The potential of SERPINA3 dynamics as a biomarker for CTRCD, deserves validation in larger cohorts.
Keywords: Anthracycline; Biomarker; Breast cancer; Cancer therapy-related cardiac dysfunction (CTRCD); Cardiotoxicity; SERPINA3.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study complies with the Declaration of Helsinki, was approved by the local ethics committee of the Antwerp University Hospital, and all subjects gave written informed consent. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Zamorano JL, Lancellotti P, Rodriguez Muñoz D, Aboyans V, Asteggiano R, Galderisi M, et al. 2016 ESC Position Paper on cancer treatments and cardiovascular toxicity developed under the auspices of the ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines. Eur J Heart Fail. 2017;19(1):9–42. - PubMed
-
- Lyon AR, López-Fernández T, Couch LS, Asteggiano R, Aznar MC, Bergler-Klein J, et al. 2022 ESC Guidelines on cardio-oncology developed in collaboration with the European Hematology Association (EHA), the European Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (ESTRO) and the International Cardio-Oncology Society (IC-OS): Developed by the task force on cardio-oncology of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2022;23(10):e333-465. - PubMed
-
- Pudil R, Mueller C, Čelutkienė J, Henriksen PA, Lenihan D, Dent S, et al. Role of serum biomarkers in cancer patients receiving cardiotoxic cancer therapies: a position statement from the Cardio-Oncology Study Group of the Heart Failure Association and the Cardio-Oncology Council of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur J Heart Fail. 2020;22(11):1966–83. - PubMed
-
- Pavo N, Raderer M, Hülsmann M, Neuhold S, Adlbrecht C, Strunk G, et al. Cardiovascular biomarkers in patients with cancer and their association with all-cause mortality. Heart. 2015;101(23):1874–80. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 1192420N/Fonds Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
- 1S33720N/Fonds Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
- G055821N/Fonds Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
- Funds Pierre Masure, Alphonse & Marie Walckiers and De Winter-Vermant 2018,/Koning Boudewijnstichting
- Funds Pierre Masure, Alphonse & Marie Walckiers and De Winter-Vermant 2018,/Koning Boudewijnstichting
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
