Molecular mechanisms of miR-192 in cancer: a biomarker and therapeutic target
- PMID: 40087755
- PMCID: PMC11908092
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-025-03666-5
Molecular mechanisms of miR-192 in cancer: a biomarker and therapeutic target
Abstract
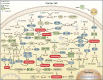
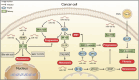
Cancer remains a major global health challenge due to its rising prevalence and high mortality rates. The field of microRNAs (miRNAs) has made significant progress in the understanding of tumorigenesis and has broadened our knowledge of their targeting, especially in cancer therapy. miRNAs, a class of small non-coding RNAs, participate in post-transcriptional gene regulation by translational inhibition or mRNA degradation. Among these, microRNA-192 (miR-192) is located on human chromosome 11q13.1, and is highly correlated with the occurrence and development of various human cancers. Dysregulation of miR-192 has been extensively studied in various pathological processes, including tumorigenesis, making it a valuable biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. The functional role of miR-192 varies across cancer types, acting as either a tumor suppressor or as an oncogene through the modulation of multiple gene expressions and downstream signaling pathways. However, the roles of miR-192 in cancer appear inconsistent across types, with current research often focused on specific genes or pathways, limiting insight into its broader impact on cellular signaling networks. Therefore, this review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of miR-192 research. The paper reviews differences in miR-192 expression in cancer and systematically summarizes the role of miR-192 in cancers. The review further explores the complex roles of miR-192 in various pathological processes, emphasizing its regulatory pathways, interaction networks, and association with tumor progression. This review also illustrates the clinical application of miR-192 as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for non-invasive cancer detection, as it is consistently present in both serum and exosomes. A comprehensive summary and analysis of the relationship between miR-192 and various cancers may provide valuable insights, potentially guiding novel approaches in clinical diagnosis, therapeutic strategies, and foundational cancer research.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Expression; Mechanism; Oncogene; Tumor suppressor; miR-192.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel R, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(3):229–63. - PubMed
-
- Ashrafizadeh M, Zarrabi A, Hushmandi K, Hashemi F, Moghadam ER, Owrang M, Hashemi F, Makvandi P, Goharrizi MASB, Najafi M, et al. Lung cancer cells and their sensitivity/resistance to cisplatin chemotherapy: role of microRNAs and upstream mediators. Cell Signal. 2021;78: 109871. - PubMed
-
- Paskeh MDA, Mirzaei S, Orouei S, Zabolian A, Saleki H, Azami N, Hushmandi K, Baradaran B, Hashmi M, Aref AR, et al. Revealing the role of miRNA-489 as a new onco-suppressor factor in different cancers based on pre-clinical and clinical evidence. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;191:727–37. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

