Actionable genetic variants in 4,198 Scottish participants from the Orkney and Shetland founder populations and implementation of return of results
- PMID: 40088892
- PMCID: PMC12081267
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2025.02.018
Actionable genetic variants in 4,198 Scottish participants from the Orkney and Shetland founder populations and implementation of return of results
Abstract
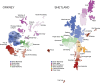
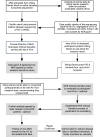
The benefits of returning clinically actionable genetic results to participants in research cohorts are accruing, yet such a genome-first approach is challenging. Here, we describe the implementation of return of such results in two founder populations from Scotland. Between 2005 and 2015, we recruited >4,000 adults with grandparents from Orkney and Shetland into the Viking Genes research cohort. The return of genetic data was not offered at baseline, but in 2023, we sent invitations to participants for consent to return of actionable genetic findings. We generated exome sequence data from 4,198 participants and used the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) v.3.2 list of 81 genes, ClinVar review, and pathogenicity status, plus manual curation, to develop a pipeline to identify potentially actionable variants. We identified 104 individuals (2.5%) with 108 actionable genotypes at 39 variants in 23 genes and validated these. Working with the NHS Clinical Genetics service, which provided genetic counseling and clinical verification of the research results, and after expert clinical review, we notified 64 consenting participants (or their next of kin) of their actionable genotypes. Ten actionable variants across seven genes (BRCA1, BRCA2, ATP7B, TTN, KCNH2, MUTYH, and GAA) have risen 50- to >3,000-fold in frequency through genetic drift in ancestral island localities. Viking Genes is one of the first UK research cohorts to return actionable findings, providing an ethical and logistical exemplar of return of results. The genetic structure in the Northern Isles of Scotland with multiple founder effects provides a unique opportunity for a tailored approach to disease prevention through genetic screening.
Keywords: Orkney; Shetland; actionable variant; exomes; founder effect; return of results.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests A.R.S. and G.T. are employees and/or stockholders of Regeneron Genetics Center or Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. L.K. is an employee of BioAge Labs and holds share options. J.S.W. has received research support from Bristol Myers Squibb and has acted as a consultant for MyoKardia, Pfizer, Foresite Labs, Health Lumen, and Tenaya Therapeutics.
Figures
References
-
- Miller D.T., Lee K., Abul-Husn N.S., Amendola L.M., Brothers K., Chung W.K., Gollob M.H., Gordon A.S., Harrison S.M., Hershberger R.E., et al. ACMG SF v3.2 list for reporting of secondary findings in clinical exome and genome sequencing: A policy statement of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) Genet. Med. 2023;25 doi: 10.1016/j.gim.2023.100866. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Venner E., Muzny D., Smith J.D., Walker K., Neben C.L., Lockwood C.M., Empey P.E., Metcalf G.A., Kachulis C., et al. All of Us Research Program Regulatory Working Group Whole-genome sequencing as an investigational device for return of hereditary disease risk and pharmacogenomic results as part of the All of Us Research Program. Genome Med. 2022;14:34. doi: 10.1186/s13073-022-01031-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schwartz M.L.B., McCormick C.Z., Lazzeri A.L., Lindbuchler D.M., Hallquist M.L.G., Manickam K., Buchanan A.H., Rahm A.K., Giovanni M.A., Frisbie L., et al. A Model for Genome-First Care: Returning Secondary Genomic Findings to Participants and Their Healthcare Providers in a Large Research Cohort. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018;103:328–337. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2018.07.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

