Comprehensive Proteomics Metadata and Integrative Web Portals Facilitate Sharing and Integration of LINCS Multiomics Data
- PMID: 40089066
- PMCID: PMC12332945
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2025.100947
Comprehensive Proteomics Metadata and Integrative Web Portals Facilitate Sharing and Integration of LINCS Multiomics Data
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Comprehensive Proteomics Metadata and Integrative Web Portals Facilitate Sharing and Integration of LINCS Multiomics Data".Mol Cell Proteomics. 2025 Jul;24(7):100995. doi: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2025.100995. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2025. PMID: 40783300 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
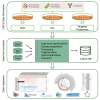
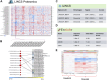
The Library of Integrated Network-based Cellular Signatures (LINCS), an NIH Common Fund program, has cataloged and analyzed cellular function and molecular activity profiles in response to >80,000 perturbing agents that are potentially disruptive to cells. Because of the importance of proteins and their modifications to the response of specific cellular perturbations, four of the six LINCS centers have included significant proteomics efforts in the characterization of the resulting phenotype. This manuscript aims to describe this effort and the data harmonization and integration of the LINCS proteomics data discussed in recent LINCS papers.
Keywords: FAIRness; LINCS data portal; LINCS proteomics metadata; P100 data; metadata harmonization; piNET.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests.: R.L.G. is on the advisory board of ProtiFi, LLC, and receives no compensation of any kind.
Figures


References
-
- Hornbeck P.V., Kornhauser J.M., Tkachev S., Zhang B., Skrzypek E., Murray B., et al. PhosphoSitePlus: a comprehensive resource for investigating the structure and function of experimentally determined post-translational modifications in man and mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:D261–D270. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

