Comparative assessment of the effects of dotinurad and febuxostat on the renal function in chronic kidney disease patients with hyperuricemia
- PMID: 40089552
- PMCID: PMC11910530
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-94020-2
Comparative assessment of the effects of dotinurad and febuxostat on the renal function in chronic kidney disease patients with hyperuricemia
Abstract
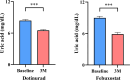
Although hyperuricemia is associated with chronic kidney disease (CKD), the impact of uric acid (UA)-lowering drugs on CKD has been controversial. Previous investigations have primarily included xanthine oxidase inhibitors; therefore, research of dotinurad, a recently developed selective urate reabsorption inhibitor, is necessary. This retrospective study included 58 patients with CKD; of these, 29 newly initiated dotinurad and 29 initiated febuxostat. The effects of dotinurad and febuxostat on the serum UA, urinary UA-to-creatinine ratio (UUCR), and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) during 3 months were analyzed to compare their impacts on renal function. Dotinurad and febuxostat decreased serum UA (8.40 ± 1.11 to 6.50 ± 0.80 mg/dL [p < 0.001] and 8.91 ± 1.21 to 6.05 ± 1.28 mg/dL [p = < 0.001], respectively). The UUCR increased after dotinurad (0.35 ± 0.15 to 0.40 ± 0.21 g/gCr [p = 0.024]); however, it decreased after febuxostat (0.33 ± 0.12 to 0.21 ± 0.06 g/gCr [p = 0.002]). The eGFR improved after dotinurad (33.9 ± 15.2 to 36.2 ± 15.9 mL/min/1.73 m2 [p < 0.001]). No change was observed after febuxostat treatment (33.4 ± 19.6 to 34.1 ± 21.6 mL/min/1.73 m2). Renal function improved only with dotinurad, thus highlighting its renoprotective effects beyond the reduction of serum UA.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; Dotinurad; Hyperuricemia; Selective urate reabsorption inhibitor; Urate transporter-1; Urinary uric acid.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

