Clinical comparison of vaginal misoprostol combined with a foley balloon versus vaginal misoprostol alone for inducing labor: a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 40089692
- PMCID: PMC11910841
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-025-07375-9
Clinical comparison of vaginal misoprostol combined with a foley balloon versus vaginal misoprostol alone for inducing labor: a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Objective: To compare the induction-to-delivery time and maternal satisfaction associated with vaginal misoprostol combined with a Foley balloon to those associated with vaginal misoprostol alone for labor induction.
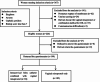
Methods: This was a prospective cohort study involving singleton full-term pregnant women with fetuses who were observed in the cephalic position; these patients were divided into a combination group (25 µg vaginal misoprostol combined with a Foley balloon, n = 94) and a misoprostol group (25 µg vaginal misoprostol, n = 105). The primary outcome was the induction-to-delivery time, and the secondary outcomes included maternal satisfaction, mode of delivery and neonatal conditions.
Results: The induction-to-delivery time was significantly lower in the combination group than in the misoprostol group (13.91 [10.85-21.48] hours vs. 17.8 [12.63-26.63] hours, respectively; P = 0.016), and this difference was still observed in analyses including only those women with vaginal births (13.40 [10.65-20.47] hours vs. 18.49 [12.91-27.00] hours, respectively; P = 0.001). Stratified analysis revealed that this benefit was particularly significant among nulliparous women. The questionnaire survey revealed similar levels of maternal satisfaction with birth experience between the combination group and the misoprostol group (69.9% vs. 66.7%, P = 0.627) but a higher rate of pain during labor induction in the combination group (16% vs. 5.8%, P = 0.02). No significant differences were observed in neonatal conditions, satisfaction rates regarding the duration of labor induction and the frequency and intensity of contractions between the groups.
Conclusion: Vaginal misoprostol combined with a Foley balloon effectively shortens the induction-to-delivery time but induces more severe pain during labor induction, thus providing overall satisfaction comparable to that of vaginal misoprostol for labor induction. An optimal scheme for labor induction should be determined according to expectations regarding the induction-to-delivery time, and the personal feelings of the pregnant women.
Keywords: Clinical comparison; Foley; Induction of labor; Misoprostol; Satisfaction.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study received approval from the Ethics Committee of the Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University (Approval Number: 2020KY420). All of the methods were performed in accordance with approved protocols and relevant guidelines and regulations. All of the participants provided signed informed consent for participating in the study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Similar articles
-
Transcervical Foley Balloon Plus Vaginal Misoprostol versus Vaginal Misoprostol Alone for Cervical Ripening in Nulliparous Obese Women: A Multicenter, Randomized, Comparative-Effectiveness Trial.Am J Perinatol. 2021 Aug;38(S 01):e123-e128. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1708805. Epub 2020 Apr 16. Am J Perinatol. 2021. PMID: 32299108 Clinical Trial.
-
Buccal vs vaginal misoprostol combined with Foley catheter for cervical ripening at term (the BEGIN trial): a randomized controlled trial.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021 May;224(5):524.e1-524.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2021.02.016. Epub 2021 Feb 19. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021. PMID: 33617796 Clinical Trial.
-
A randomized trial comparing vaginal misoprostol versus Foley catheter with concurrent oxytocin for labor induction in nulliparous women.Am J Perinatol. 2004 Apr;21(3):139-46. doi: 10.1055/s-2004-823777. Am J Perinatol. 2004. PMID: 15085496 Clinical Trial.
-
Foley catheter versus vaginal misoprostol: randomized controlled trial (PROBAAT-M study) and systematic review and meta-analysis of literature.Am J Perinatol. 2014 Feb;31(2):145-56. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1341573. Epub 2013 Apr 5. Am J Perinatol. 2014. PMID: 23564065 Clinical Trial.
-
Misoprostol combined with cervical single or double balloon catheters versus misoprostol alone for labor induction of singleton pregnancies: a meta-analysis of randomized trials.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020 Oct;33(20):3453-3468. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2019.1574741. Epub 2019 Feb 10. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020. PMID: 30741051
References
-
- Korb D, Renard S, Morin C, Merviel P, Sibony O. Double-balloon catheter versus prostaglandin for cervical ripening to induce labor after previous Cesarean delivery. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2020;301(4):931–40. - PubMed
-
- Priyadarshini A, Jaiswar SP, Singh A, Singh S. Comparative outcome of induced labor by intracervical Foley catheter with Misoprostol versus Misoprostol alone. J COMP EFFECT RES. 2019;8(1):55–9. - PubMed
-
- Kumar N, Haas DM, Weeks AD. Misoprostol for labour induction. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2021;77:53–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources