Targeted activation of ErbB4 receptor ameliorates neuronal deficits and neuroinflammation in a food-borne polystyrene microplastic exposed mouse model
- PMID: 40089796
- PMCID: PMC11910855
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-025-03406-6
Targeted activation of ErbB4 receptor ameliorates neuronal deficits and neuroinflammation in a food-borne polystyrene microplastic exposed mouse model
Abstract
The impact of polystyrene microplastics (PS-MPs) on the nervous system has been documented in the literature. Numerous studies have demonstrated that the activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor 4 (ErbB4) is crucial in neuronal injury and regeneration processes. This study investigated the role of targeted activation of ErbB4 receptor through a small molecule agonist, 4-bromo-1-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid (C11H7BrO3, E4A), in mitigating PS-MPs-induced neuronal injury. The findings revealed that targeted activation of ErbB4 receptor significantly ameliorated cognitive behavioral deficits in mice exposed to PS-MPs. Furthermore, E4A treatment upregulated the expression of dedicator of cytokinesis 3 (DOCK3) and Sirtuin 3 (SIRT3) and mitigated mitochondrial and synaptic dysfunction within the hippocampus of PS-MPs-exposed mice. E4A also diminished the activation of the TLR4-NF-κB-NLRP3 signaling pathway, consequently reducing neuroinflammation. In vitro experiments demonstrated that E4A partially alleviated PS-MPs-induced hippocampal neuronal injury and its effects on microglial inflammation. In conclusion, the findings of this study indicate that targeted activation of ErbB4 receptor may mitigate neuronal damage and subsequent neuroinflammation, thereby alleviating hippocampal neuronal injury induced by PS-MPs exposure and ameliorating cognitive dysfunction. These results offer valuable insights for the development of potential therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Cognitive dysfunction; ErbB4 receptor; Mitochondrial damage; Neuroinflammation; Neuronal damage; PS-MPs; Small molecule.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: All procedures were conducted according to the Ethics Committee of Jiangnan University Wuxi Medical College. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
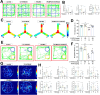
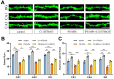
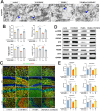
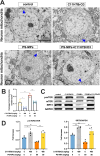



References
-
- Zhao B, Rehati P, Yang Z, Cai Z, Guo C, Li Y. The potential toxicity of microplastics on human health. Sci Total Environ. 2024;912:168946. 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.168946. - PubMed
-
- Allouzi MMA, Tang DYY, Chew KW, Rinklebe J, Bolan N, Allouzi SMA, et al. Micro (nano) plastic pollution: the ecological influence on soil-plant system and human health. Sci Total Environ. 2021;788:147815. 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147815. - PubMed
-
- Cox KD, Covernton GA, Davies HL, Dower JF, Juanes F, Dudas SE. Human consumption of microplastics. Environ Sci Technol. 2019;53(12):7068–74. 10.1021/acs.est.9b01517. - PubMed
-
- Senathirajah K, Attwood S, Bhagwat G, Carbery M, Wilson S, Palanisami T. Estimation of the mass of microplastics ingested - A pivotal first step towards human health risk assessment. J Hazard Mater 404(Pt B). 2021;124004. 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124004. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- gzhlyj 2023-04/Guizhou Nursing Vocational College Foundation
- gzwkj 2022-518/Science and Technology Foundation of Guizhou Provincial Health Committee
- JSSCRC 2021533/Jiangsu Province Shuangchuang Talent Plan
- 82301581/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 1285081903200020/the Research Start-up Fund of Jiangnan University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

